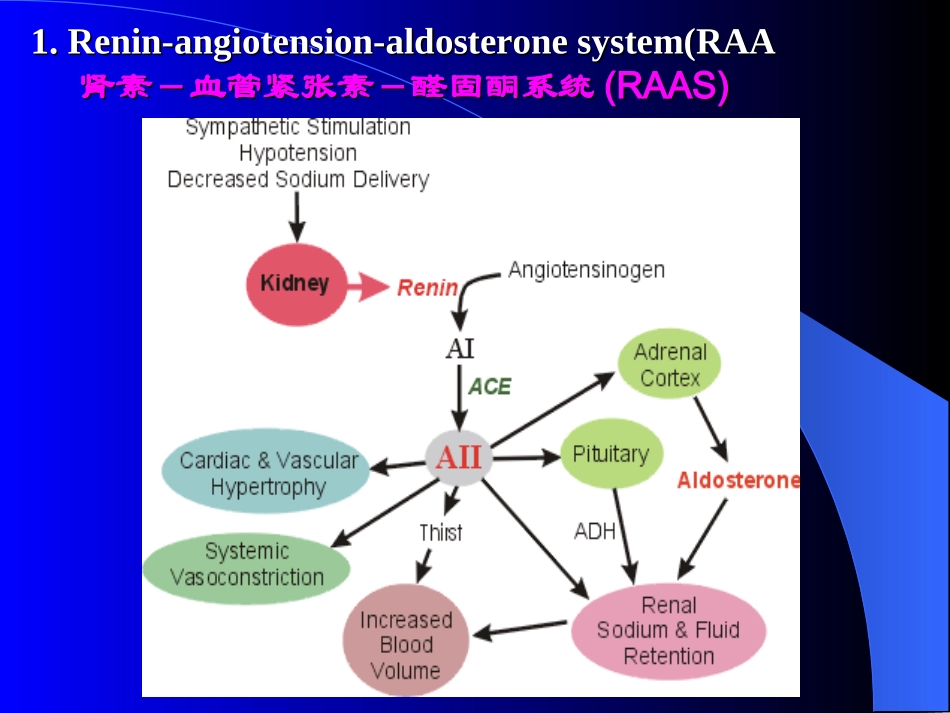
II.HumoralregulationofII.Humoralregulationofcardiovascularsystemcardiovascularsystem心血管活动的体液调节心血管活动的体液调节1.肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统(RAAS)2.肾上腺素和去甲肾上腺素3.血管升压素4.血管内皮生成的活性物质5.心房钠尿肽6.激肽释放酶-激肽系统1.Renin-angiotension-aldosteronesystem(RAA1.Renin-angiotension-aldosteronesystem(RAA肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统((RAAS)RAAS)交感神经兴奋低血压Na+↓肾球旁细胞分泌肾素↑血管紧张素原AI渴觉AIIADH心肌肥大血管增生全身血管收缩血容量↑肾脏水钠潴留下丘脑肾上腺皮质醛固酮ACE((11))AngiotoninIIAngiotoninII血管紧张素血管紧张素IIII(AII)(AII)angiotensinogen(α2-globulin)renin(kidney)angiotensin(decapeptide)Ⅰconvertingenzyme(pneumoangiogram)angiotensin(octapeptide)+ⅡAT1receptorangiotensinaseAangiotensin(heptapeptide)Ⅲa.Theformationofangiotonin血管紧张素生成过程血管紧张素原(肝合成)↓肾素(肾近球细胞分泌)血管紧张素Ⅰ(10肽)↓(转化酶,主要在肺血管)血管紧张素Ⅱ(8肽)+AT1受体↓血管紧张素酶A血管紧张素III(7肽)b.b.PhysiologicalfunctionofangiotensinⅡPhysiologicalfunctionofangiotensinⅡ血管紧张素Ⅱ的生理作用血管紧张素Ⅱ的生理作用①Thesystemicarteriolescontractsandtheperipheralresistanceincreases.全身微动脉收缩,外周阻力↑。②Theveinscontractsandthereturnedbloodincreases.静脉收缩,回心血量↑。③Prejunctionalmodulation,promotethesympatheticnerveendingtoexcreteNA.接头前调制,促进交感神经末梢释放NA。④ActiononthespecificreceptorsofCNS,thesympathesisvasoconstrictortone↑.作用于中枢特定受体,交感缩血管紧张↑。⑤Stimulatetheformationandexcretionofaldosterone,thereabsorptionofsodiumandfluidincreasesandthustheBPincreasestoo.刺激醛固酮生成分泌,水钠重吸收↑,血压↑。(2)Aldosterone醛固酮Synthesisposition:adrenalcortexZGcell合成部位:肾上腺皮质球状带细胞criticalorgan:distaltubule、collectingduct靶器官:远曲小管、集合管Function:tokeepNa+andexcreteK+.作用:保Na+排K+作用。mechanismofaction作用机制醛固酮促进小管上皮细胞Na+泵运转促进生化氧化提供ATP增加管腔膜对Na+通透性促进Na+的主动重吸收(保Na+)造成小管腔内负电位K+被分泌到小管液(排K+)2.Adrenaline(Adr)andnoradrenaline(NA)肾上腺素和去甲肾上腺素Synthesispostion:合成部位(1)adrenalmedulla肾上腺髓质Adr:80%,NE:20%肾上腺素:80%,去甲肾上腺素:20%(2)adrenergicnerveending肾上腺素能神经末梢SecreteNAonly.仅分泌少量的NA入血。肾上腺素强心药去甲肾上腺素升压药3.vasopressin(Antidiuretichormone)血管升压素(抗利尿激素)Synthesisposition:supraopticnucleusandparaventricularnucleus.Storeinposteriorpituitaryglandandreleasetobloodstream.合成部位:在下丘脑的视上核和室旁核合成。在神经垂体后叶贮存,释放到血液中发挥作用。V1receptor:constrictionofbloodvesselincreaseinbloodpressure.结合V1受体:血管收缩,血压↑。V2receptor:reabsorptionofH2Ofromcollectingductincreases.结合V2受体:肾集合管对水的重吸收↑。Physicalfunction生理功能Innormalcondition,theincreaseinthelevelofADHinplasmafirstlyinducestheeffectofantidiuresis,andonlywhenitslevelincreasesdefinitely,theBPincreases.ADHplaysanimportantroleintheregulationofthevolumeofextracellularfluid.Undertheconditionofwaterbearing,waterdepletionandbloodloss,thesecretionofADHincreasestokeepthenormalvolumeofbodyfluidandmaintainthenormalBP.正常情况下,血浆中ADH浓度升高时首先出现抗利尿效应,当其血浆浓度明显升高时,才引起血压升高。ADH对体内细胞外液量的调节起重要作用。在禁水、失水、失血等情况下,ADH释放增加,保留体内液体量,维持动脉血压。4.Endothelium-...