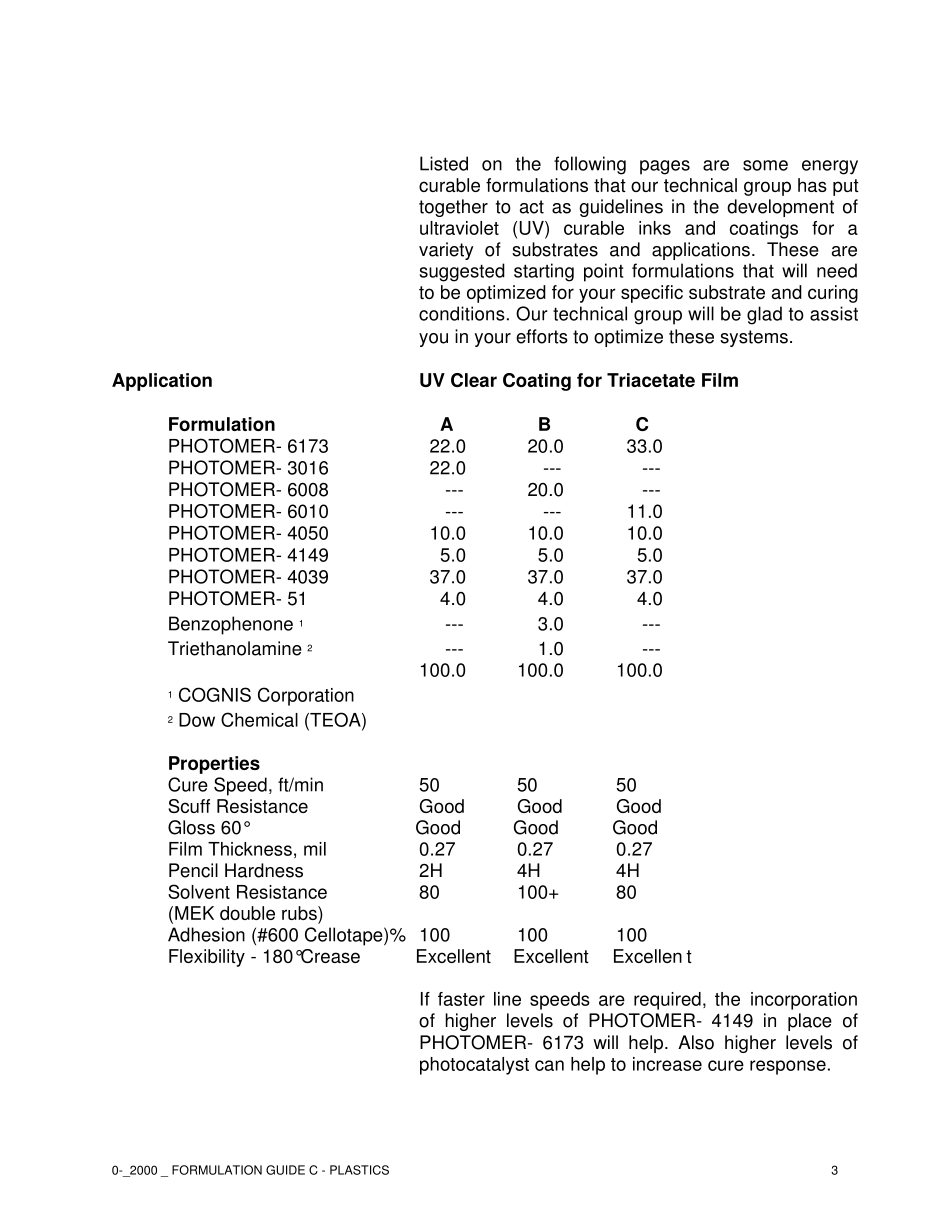
0-_2000 _ FORMULATION GUIDE C - PLASTICS1FORMULATION GUIDE C - PLASTICSUseToday’s emerging technologies require new types of plastics that meet specific requirements for both structural as well as decorative applications. These plastic substrates can be sensitive to heat as well as certain solvents, limiting the types of coating equipment that can be used with them. Energy Curable coatings are a perfect fit for these new plastics as long as sufficient bonding can be generated between the substrate and coating.In certain cases such as with polyolefins (polyethylene/polypropylene), the surface must be pretreated either through corona discharge or flame treatment. Satisfactory adhesion for other plastics such as polycarbonate, polyester, acrylic, vinyl or polystyrene, can be achieved through the proper choice of multifunctional monomers and resin backbones.Reactive diluents with low surface tension which effectively wet out the plastic substrate and which exhibit low shrinkage characteristics can be employed so that stresses developed during curing are minimized.As with any type of coating the use of additives is very common and necessary in obtaining the maximum benefits from coating and ink properties. In the development of matted finishes, the incorporation of a silica product will reduce the gloss to desired levels. One must pay attention to additive particle size to obtain the best performance without raising the viscosity of the formulation too high. Incorporation of leveling agents such as PERENOL- F-40 (COGNIS), wetting agents such as fluorochemical Fluorad FC-430 (3M Co.) or the use of defoamers DEHYDRAN- 1208 or FOAMASTER- 0-_2000 _ FORMULATION GUIDE C - PLASTICS2PC (COGNIS) will help facilitate good le...