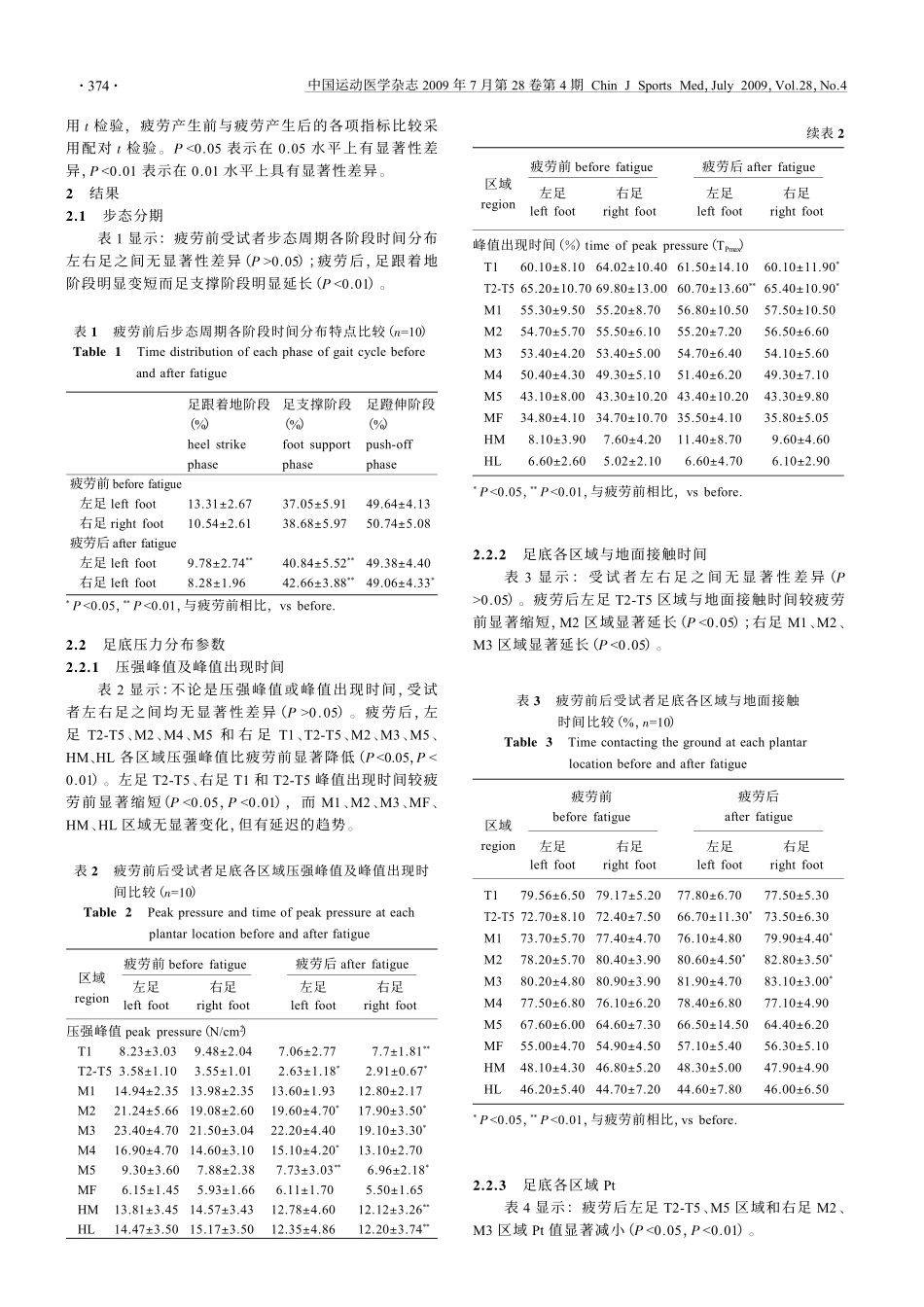
中国运动医学杂志2009年7月第28卷第4期ChinJSportsMed,July2009,Vol.28,No.4运动性疲劳(以下简称疲劳)是指人体在一段时间运动后出现的一种组织器官甚至整个机体的工作能力暂时降低的现象,是一种运动过程中普遍存在的生理现象[1]。美国足部医学会的研究报告显示,一个正常人在跑步时足部所承受的地面反作用力达到体重的3~4倍[2]。足底与支撑面之间的压力分布反映了下肢乃至全身的生理、结构和功能等方面的信息。人在疲劳时,步态会发生相应的改变,从而增大运动损伤的几率。目前,对疲劳的研究主要是对其产生机制、检测手段、消除方法等方面的研究,研究的指标主要集中于生理闫松华杨进刘志成首都医科大学生物医学工程学院(北京100069)运动性疲劳对健康男大学生足底压力分布的影响摘要目的:分析运动性疲劳对健康男大学生足底压力分布的影响,为科学指导锻炼提供依据。方法:10名普通男大学生沿400米跑道慢跑至中度疲劳,应用0.5米footscan誖USB平板测试系统对受试者运动性疲劳产生前后足底压力分布情况进行测试。结果:与疲劳前相比,运动疲劳后,(1)受试者足跟着地阶段明显变短,足支撑阶段明显变长;(2)左足T2-T5、M2、M4、M5和右足T1、T2-T5、M2、M3、M5、HM、HL各区域与地面的压强峰值显著降低;左足T2-T5区域、右足T1和T2-T5区域与地面压强峰值出现时间显著缩短,而其它部位压强峰值出现时间有延迟趋势;(3)左足T2-T5区域与地面接触时间显著缩短,M2区域显著延长;右足M1、M2、M3区域显著延长;(4)左足T2-T5区域与地面的接触面积显著减小,T1、M3、M5区域显著增大,而其它部位均有增大的趋势;右足除M3显著减小外,其它区域均表现出下降的趋势;(5)左足T2-T5、M5区域和右足M2、M3区域所受压强在时间上的积累(Pt)显著减小;(6)足平衡总体上呈现内外翻程度增大的变化趋势,但10名受试者中有3例疲劳前后的变化不明显。结论:运动性疲劳导致下肢肌肉力量减弱等生理机能下降,从而引起步态分期、足底压力分布参数、足平衡等发生相应变化。关键词运动性疲劳;健康男大学生;足底压力分布EffectsofExercise-inducedFatigueontheDynamicPlantarPressureDistributioninHealthyMaleCollegeStudentsYanSonghua,YangJin,LiuZhichengBiomedicalEngineeringSchool,CapitalMedicalUniversity,Beijing,China100069AbstractObjectiveTheeffectsofexercise-inducedfatigueontheplantarpressuredistributionofhealthymalecollegestudentswasanalyzedinthisstudy.MethodsTenhealthymalecollegestudentsjoggedaroundthe400mrunwayuntilappearingoffatigue.Footscan誖USBplatesystemwasusedtotesttheplantarpressureofthe10subjectsbeforeandafterfatigue.ResultsAfterrunning:(1)heelstrikephaseshortenedandfootsupportphaseprolonged.(2)PeakpressuresagainstthegroundatT2-T5,M2,M4andM5oftheleftfoot,andatT1,T2-T5,M2,M3,M5,HMandHLoftherightfootdecreasedevidently;timeofpeakpressureagainstthegroundatT2-T5oftheleftfootandatT1andT2-T5oftherightfootdecreasedevidently,whilethetimeofpeakpressureatotherregionsincreasedevidently.(3)ThedurationofcontactingthegroundatT2-T5oftheleftfootdecreased;andatM2oftheleftfootandatM1,M2andM3oftherightfootincreasedevidently.(4)TheareacontactingthegroundatT2-T5oftheleftfootdecreased,andatT1,M3andM5decreasedevidently.Thoseattheotherregionsincreasedinsomeextent.Fortherightfoot,theareacontactingthegroundbesideatM3decreasedevidently,thoseattheotherregionsincreasedonlyinsomeextent.(5)IntegrationofpressuresanddurationsatT2-T5andM5oftheleftfoot,andatM2andM3oftherightfootdecreasedevidently.(6)Increasedpronation-supinationtrendappearedin7ofthe10subjects.ConclusionDecreasedphysicalfunctionincludingtheweakeningofmusclestrengthoflowerlimbscausedbyexercised-inducedfatiguecouldleadtovariationofgaitcycleandposturalimbalance.Ke...