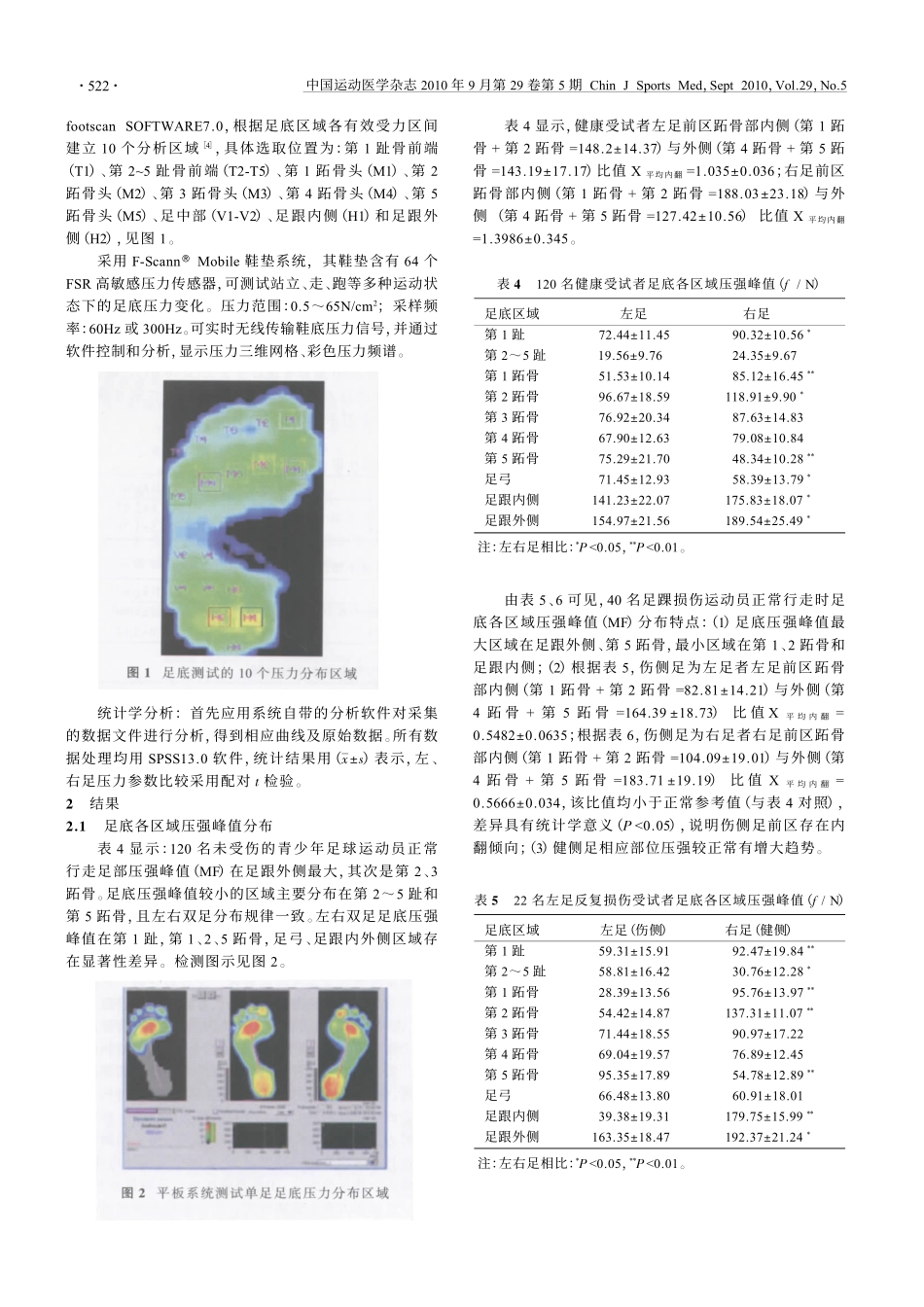
中国运动医学杂志2010年9月第29卷第5期ChinJSportsMed,Sept2010,Vol.29,No.5周军杰1俞光荣2曹成福1陈贤奇1庞金辉1石继祥11上海中医药大学附属普陀医院骨科(上海200062)2上海同济大学附属同济医院骨科足踝部反复损伤青少年足球运动员FootScan足底压力分析摘要目的:探讨足底压力分析在青少年运动损伤领域的应用价值。方法:2008年1月~2009年10月期间,在上海市普陀区青少年运动训练基地将40名16~19岁足踝部损伤3次以上的青少年足球运动员分为左足损伤和右足损伤两组,采用美国Tekscan公司的F-Scan三维动态足底压力步态分析系统,进行静、动态足底压力测试,测试数据与前期120名足踝部未损伤的健康青少年足球运动员正常数据进行对比分析。所有受试者均脱鞋袜,以个人正常步态自然行走,测量双脚各3次静、动态足底压力,测量指标为足底每个区域的压强峰值、接触时间负荷,计算足底各区域的压强峰值和负荷分布、重心轨迹特征。结果:青少年足球运动员损伤侧足底压力分布特征:(1)足底压强峰值最大区域在第5跖骨、足跟外侧;(2)足前区跖骨部的内侧与外侧比值低于正常参考值,差异具有统计学意义,足前区存在内翻倾向;(3)足部压力重心变化有向足前区转移的趋势,双足压强变化不对称;(4)足踝反复损伤者前足撑地时间延长,后足撑地时间减少。结论:足踝反复损伤青少年足球运动员足底压强变化不稳定,双足压强变化不对称;损伤足与正常对照差异显著,足部压力重心变化有向足前区转移的趋势,前足撑地时间延长,后足撑地时间减少,可能是为了减少损伤侧足踝关节的载荷而采取的保护性机制。足底压力分析在预防青少年足球运动员足踝反复损伤方面有临床价值。关键词青少年;足底压力;临床应用;运动医学AnalysisonPlantarPressureofAdolescentSoccerPlayerswithRepeatedFootandAnkleInjuryZhouJunjie1,YuGuangrong2,CaoChengfu1,ChenXianqi1,PangJinhui1,ShiJixiang11DepartmentofOrthopaedics,PutuoHospital,ShanghaiTraditionalChineseMedicineUniversity,Shanghai,China2000622DepartmentofOrthopaedics,TongjiHospital,TongjiUniversity,Shanghai,China200065AbstractAimToinvestigatetheclinicalvalueofplantarpressureanalysisinadolescentssoccerplayerswithrepeatedfootandankleinjuries.MethodsFromJanuary,2008toOctober,2009,40adolescentssoccerplayers(aged16-19years)withatleast3timesoffootandankleinjuriesinShanghaiPutuoYouthSportsTrainingBasewereenrolledinthisstudy.Theyweredividedintotwogroups:leftfootinjurygroupandrightfootinjurygroup.F-ScanofTekscanCo.wasappliedtomeasurethestaticanddynamicplantarpressureoftheinjuredsubjects.Threestaticanddynamicdataobtainedfrominjuredsubjectswerecomparedwiththatfrom120age-matchedhealthyadolescentsoccerplayers.Peakpressureinvariouscontactareasandcontactdurationweremeasured,andthenaveragepeakplantarforceofvariouscontactareasandloaddistributionwerecalculated.ResultsThecharacteristicsofplantarpressuredistributionininjuredsideofadolescentsoccerplayerincluded:(1)Thepeakplantarpressuremostlylocatedinthe5thmetatarsalandlateralheelareas;(2)Thevaluesofinnerandlateralsidesattheanteriormetatarsalareaweresignificantlydifferentfromthenormalreferencevalues,andtherewasavarustendencyofpropodium;(3)Therewasatendencyofanteriorshifttowardofcenterofgravity,andanasymmetryofpressurebetweenleftandrightfoots.(4)Thecontactdurationinpropodiumprolongedandshortenedinmetapodium.ConclusionPlantarpressureanalysisforyoungfootballplayershascertainclinicalvalueinthepreventionofchronicankleinjury.Keywordsadolescent,footinjury,ankleinjury,footpressure基金项目:上海市重点学科资助项目(T0303),上海市体育科技腾飞计划项目(07FT004)通信作者:周军杰,Email:boysroger@126.com足踝部损伤为最常见的运动性损伤之一...