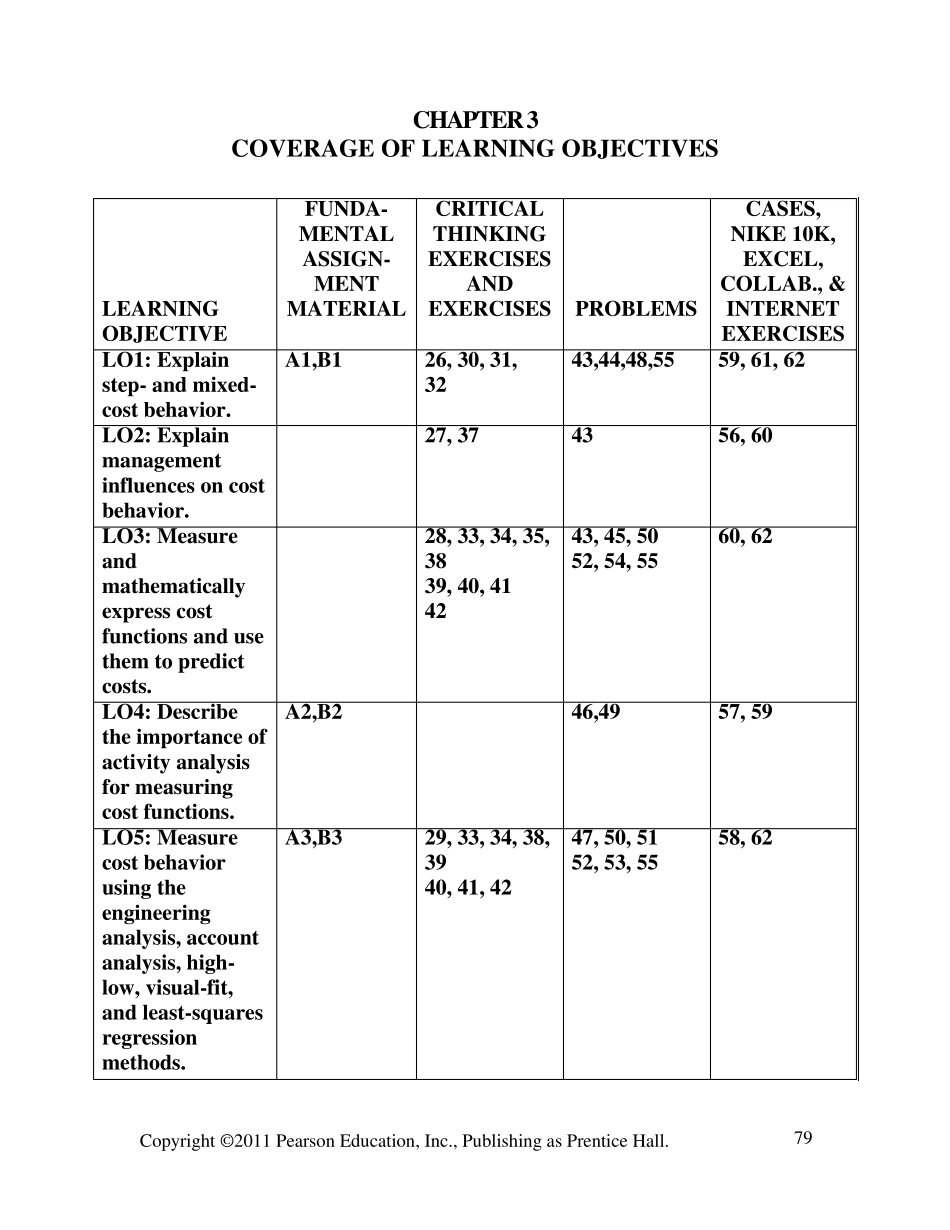
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Prentice Hall. 79 CHAPTER 3 COVERAGE OF LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OBJECTIVE FUNDA- MENTAL ASSIGN-MENT MATERIAL CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISES AND EXERCISES PROBLEMS CASES, NIKE 10K, EXCEL, COLLAB., & INTERNET EXERCISES LO1: Explain step- and mixed-cost behavior. A1,B1 26, 30, 31, 32 43,44,48,55 59, 61, 62 LO2: Explain management influences on cost behavior. 27, 37 43 56, 60 LO3: Measure and mathematically express cost functions and use them to predict costs. 28, 33, 34, 35, 38 39, 40, 41 42 43, 45, 50 52, 54, 55 60, 62 LO4: Describe the importance of activity analysis for measuring cost functions. A2,B2 46,49 57, 59 LO5: Measure cost behavior using the engineering analysis, account analysis, high-low, visual-fit, and least-squares regression methods. A3,B3 29, 33, 34, 38, 39 40, 41, 42 47, 50, 51 52, 53, 55 58, 62 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Prentice Hall. 80 CHAPTER 3 Measurement of Cost Behavior 3-A1 (20-25 min.) Some of these answers are controversial, and reasonable cases can be built for alternative classifications. Class discussion of these answers should lead to worthwhile disagreements about anticipated cost behavior with regard to alternative cost drivers. 1. (b) Discretionary fixed cost. 2. (e) Step cost. 3. (a) Purely variable cost with respect to revenue. 4. (a) Purely variable cost with respect to miles flown. 5. (d) Mixed cost with respect to miles driven. 6. (c) Committed fixed cost. 7. (b) Discretionary fixed cost. 8. (c) Committed fixed cost. 9. (a) Purely variable cost with respect to cases of 7-Up. 10. (b) Discretionary fixed cost. 11. (b) Discretionary fixed cost. 3-A2 (25-30 min.) 1. Suppo...