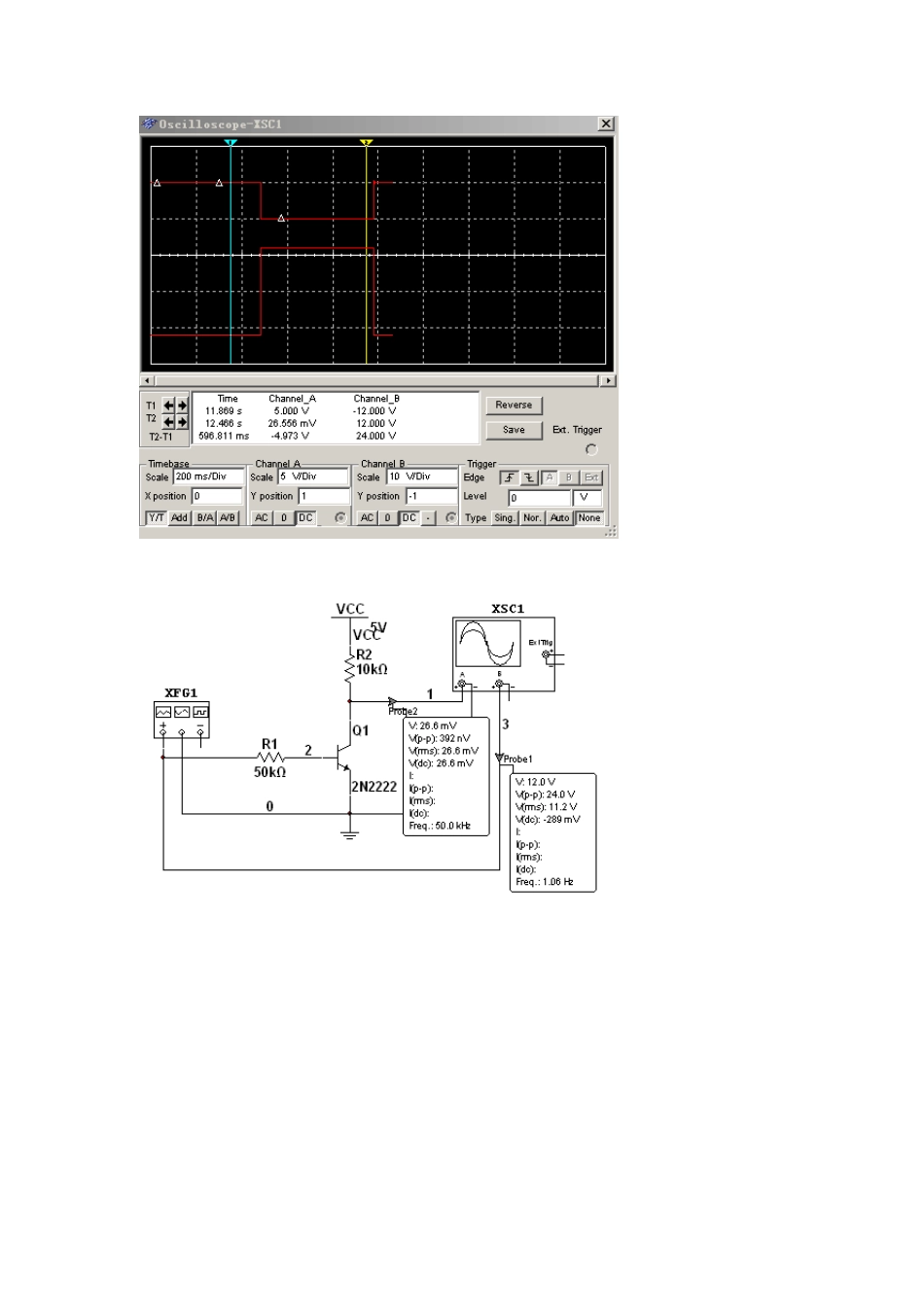
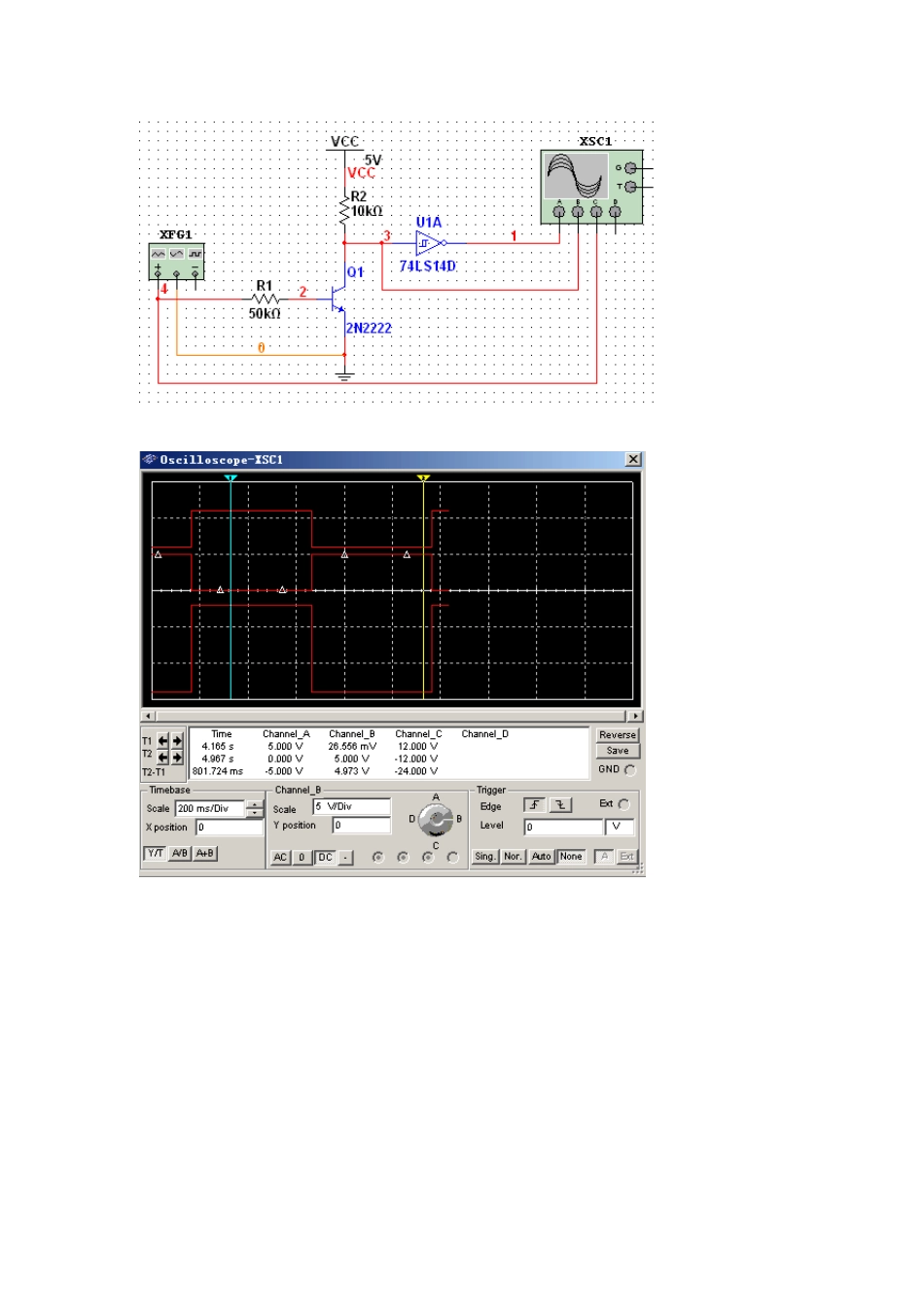
双极性三极管开关特性 晶体三极管工作于截止区时,内阻很大,相当于开关断开状态;工作于饱和区时,内阻很低,相当于开关接通状态。三极管开关电路如图 2.2.2(a)示。 输入控制信号 为矩形电压脉冲,电源电压 ,输出信号为 ,三极管开关电路输入输出波形如图 2.2.2(b)。 下实例中为 12V的开关控制信号,为单片机可接收的 TTL信号,为了与输入控制信号一致,加入反相器 74LS14。 Transistors A Transistor is a solid-state device designed to control DC current. Transistors are most commonly found in low DC powered sensors as the output switch. There are two types of transistors - NPN and PNP. The figure below shows a NPN (Current Sink) Open Collector Transistor Figure 1: Sensor NPN Output Output Style Depending on model, incremental encoders are available with several different electrical output styles. Choice of signal depends on receiving instrument and cable distance. Line driver outputs with complimentary outputs can be used with longer cables as noise spikes can be cancelled. NPN Uses an NPN type transistor and an internal resistor pulling up to the power supply rail. The output is an active voltage. NPN Open Collector Uses an NPN type transistor but without an internal pull up resistor to the supply rail. The output is passive so a separate power supply can be used. PNP Uses a PNP type transistor and an internal resistor pulling down to zero volts. PNP Open Collector Uses a PNP type transistor but without an internal pull down resistor to zero volts. Push Pull A problem with NPN and PNP type outputs is the high output impedance. This can be solved by a complementary output allowing better switching to zero and positive supply rails. Line Driver This output style has two complimentary outputs per channel allowing better transmission in noisy environments a...