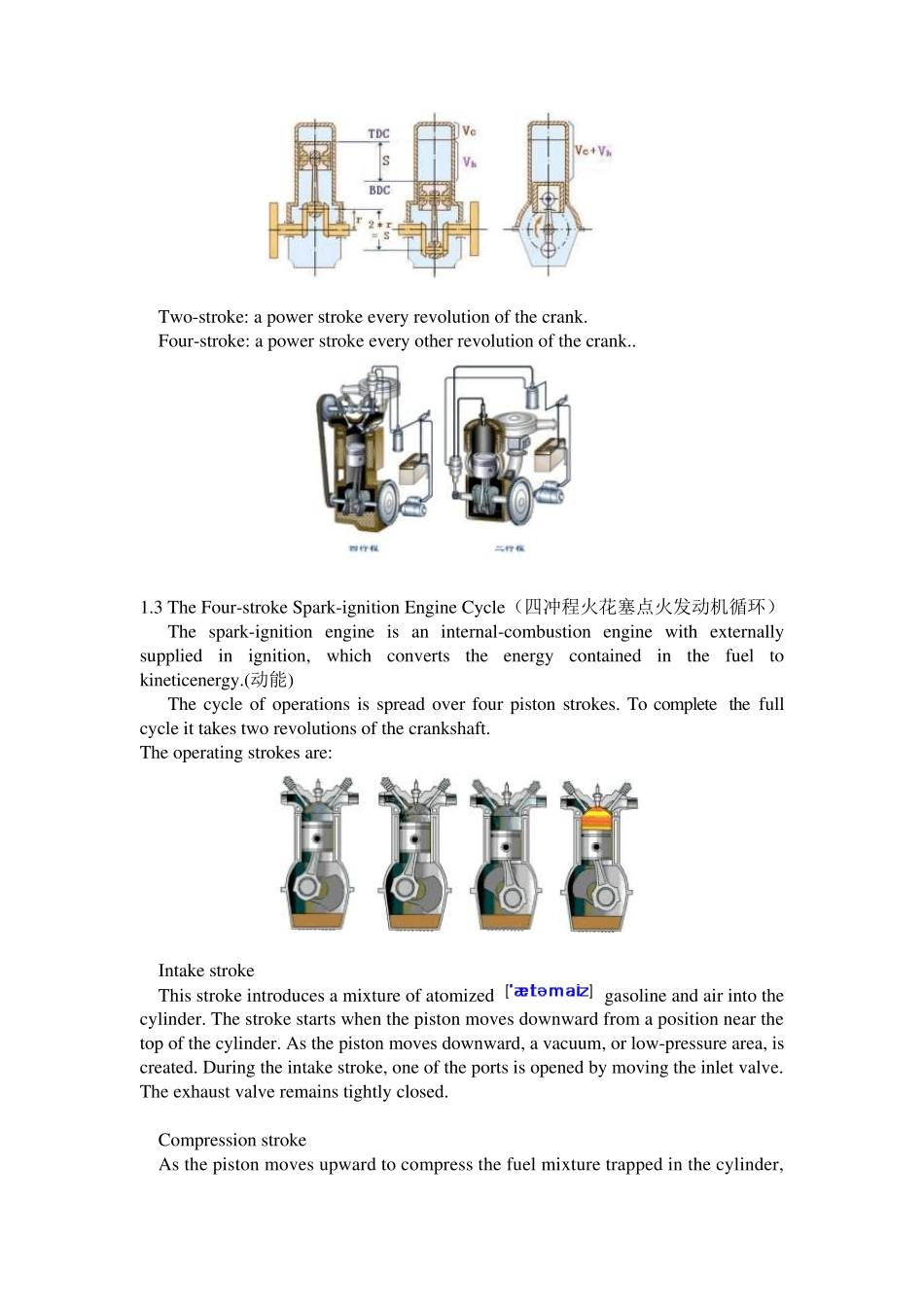
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (内燃机) 1 principle of operation (工作原理 or 操作原理) 1.1 Engine and power(发动机和功率) Engine is used to produce power. The chemical energy in fuel is converted to heat by the burning of the fuel at a controlled rate. This process is called combustion. If engine combustion occurs with the power chamber, the engine is called internal combustion engine. If combustion takes place outside the cylinder, the engine is called an external combustion engine. Engine used in automobiles are internal combustion heat engines. Heat energy released in the combustion chamber raises the temperature of the combustion gases with the chamber. The increase in gas temperature causes the pressure of the gases to increase. The pressure developed within the combustion chamber is applied to the head of a piston to produce a usable mechanical force, which is then converted into useful mechanical power. 1.2 Engine Terms (发动机术语) Linking the piston by a connecting rod to a crankshaft causes the gas to rotate the shaft through half a turn. The power stroke “uses up” the gas, so means must be provided to expel the burnt gas and recharge the cylinder with a fresh petrol-air mixture:this control of gas movement is the duty of the valves; an inlet valve allows the new mixture to enter at the right time and an exhaust valve lets out the burnt gas after the gas has done its job. Engine terms are: TDC(Top Dead Center): the position of the crank and piston when the piston is farther away from the crankshaft. BDC(Bottom Dead Center): the position of the crank and piston when the piston is nearest to the crankshaft. Stroke: the distance between BDC and TDC; stroke is controlled b...