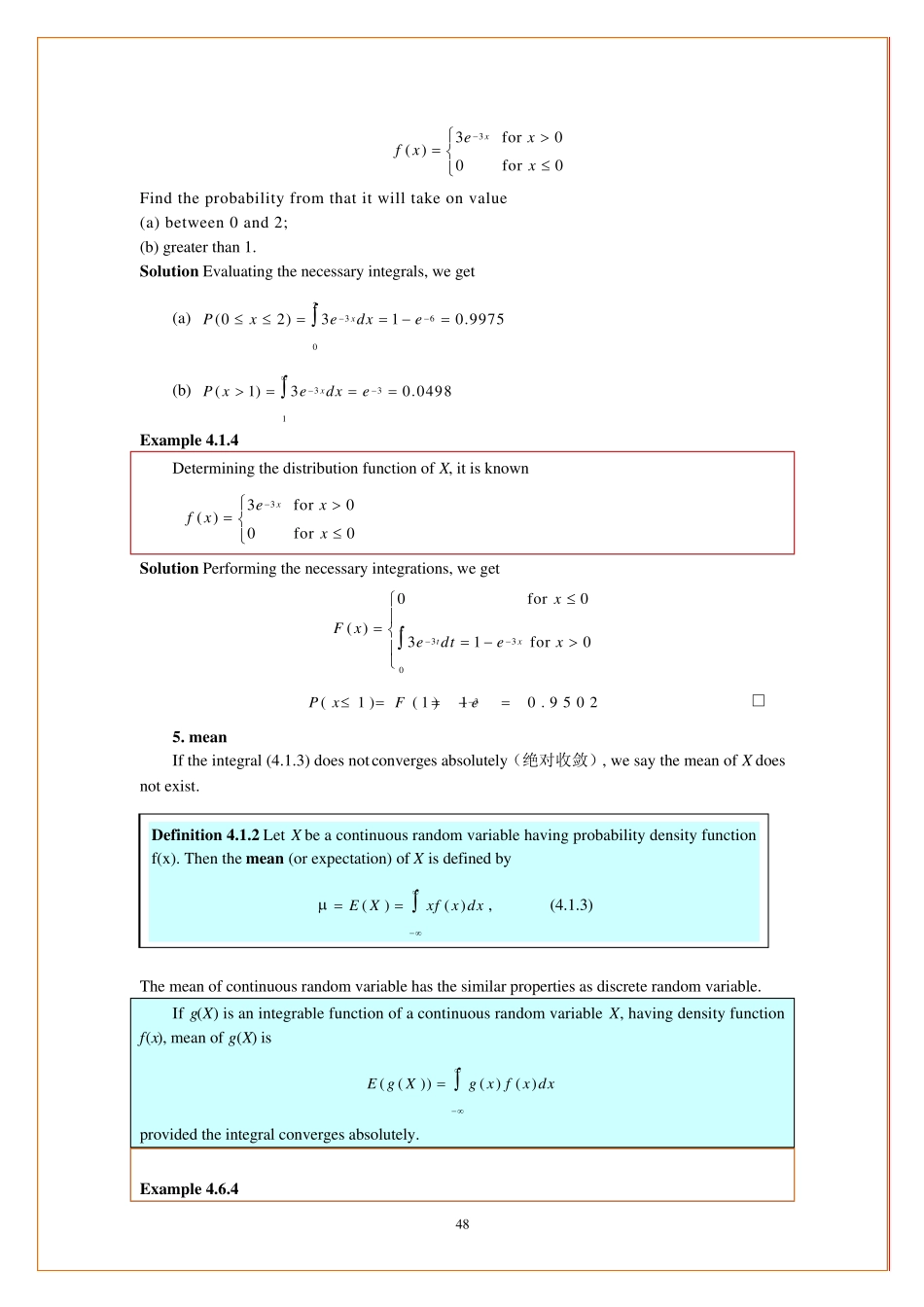
46 4. Continuous Random Variable 连续型随机变量 Continuous random variables appear when we deal will quantities that are measured on a continuous scale. For instance, when we measure the speed of a car, the amount of alcohol in a person's blood, the tensile strength of new alloy. We shall learn how to determine and work with probabilities relating to continuous random variables in this chapter. We shall introduce to the concept of the probability density function. 4.1 Continuous Random Variable 1. Definition Definition 4.1.1 A function f(x ) defined on (, ) is called a probability density function (概率密度函数)if: (i) ( )0 for any fxxR; (ii) f(x ) is intergrable (可积的) on (, ) and ( )1fx dx. Definition 4.1.2 Let f(x ) be a probability density function. If X is a random variable having distribution function ( )()( )xF xP Xxf t dt , (4.1.1) then X is called a continuous random variable having density function f(x ). In this case, 2112()( )xxP xXxf t dt . (4.1.2) 2. 几何意义 ( )()((,) |, 0())( )xF xP XxPX YXxYfXf t dt 47 2112()( )xxP xXxf t dt 3. Note In most applications, f(x ) is either continuous or piecewise continuous having at most finitely many discontinuities. Note 1 For a random variable X, we have a distribution function. If X is discrete, it has a probability distribution. If X is continuous, it has a probability density function. Note 2 Let X be a continuous random variable, then for any real number x , ()0P Xx. xxdxxfxXP)()(0 0)()(0lim0xxdxxfxXP ()()()()P aXbP aXbP aXbP aXb 4. Example Example 4.1.2 Find k so that the following can serve as the pro...