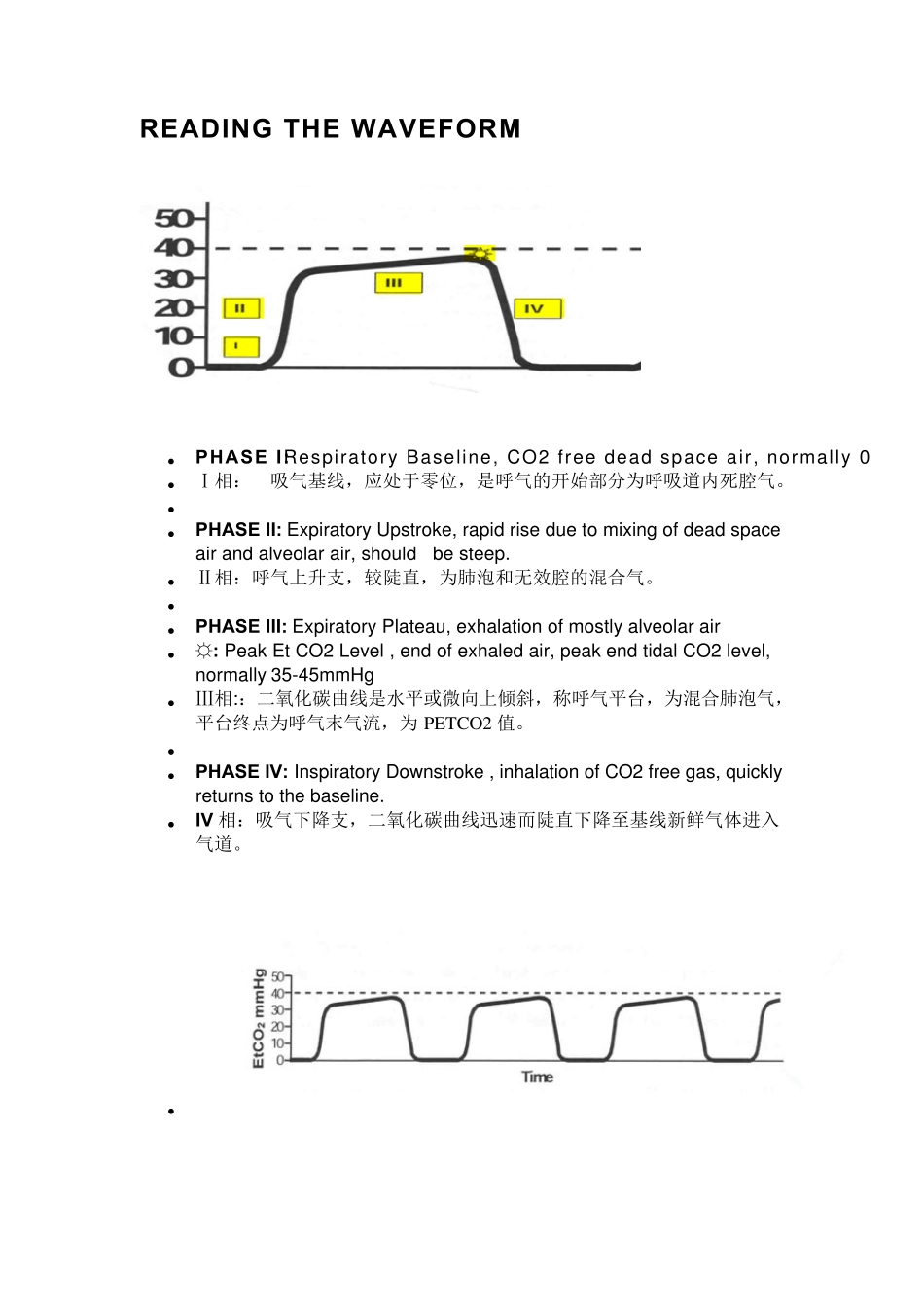
READING THE W AVEFORM PHASE I: Respiratory Baseline, CO2 free dead space air, normally 0 Ⅰ相: 吸气基线,应处于零位,是呼气的开始部分为呼吸道内死腔气。 PHASE II: Expiratory Upstroke, rapid rise due to mixing of dead space air and alveolar air, should be steep. Ⅱ相:呼气上升支,较陡直,为肺泡和无效腔的混合气。 PHASE III: Expiratory Plateau, exhalation of mostly alveolar air ☼: Peak Et CO2 Level , end of exhaled air, peak end tidal CO2 level, normally 35-45mmHg Ⅲ相::二氧化碳曲线是水平或微向上倾斜,称呼气平台,为混合肺泡气,平台终点为呼气末气流,为 PETCO2 值。 PHASE IV: Inspiratory Downstroke , inhalation of CO2 free gas, quickly returns to the baseline. IV 相:吸气下降支,二氧化碳曲线迅速而陡直下降至基线新鲜气体进入气道。 Hyperventilation (过度通气) In hyperventilation, the capnograph starts normal but as the rate becomes faster the waveforms become closer together and the level of end tidal CO2 begins to decrease. The most common cause of hyperventilation is over zealous bagging of a patient with an advanced airway placed. When decreasing end tidal CO2 levels are noted, simply slow the rate in which the patient is being ventilated until end tidal CO2 levels return to normal. In the spontaneously breathing patient, increasing respiratory rate and decreasing end tidal CO2 levels can be a sign of hyperventilation syndrome or pulmonary embolism. 过度通气,波形一开始是正常但是随着频率越来越快,波形就变成越来越靠近,二氧化碳分压水平越呈下降趋势。如果呼气末二氧化碳分压水平及时不断下降被发现,只需调低病人机械通气的频率,至到呼气末二氧化碳分压达到正常水平。如果在有自主呼吸的病人中,呼吸频率增加和呼气末二氧化碳分压下降是过度通气综合征和肺栓塞的的一个体征。 Hypoventilation(通气不足) Hypoventilation is seen when there is increasin...