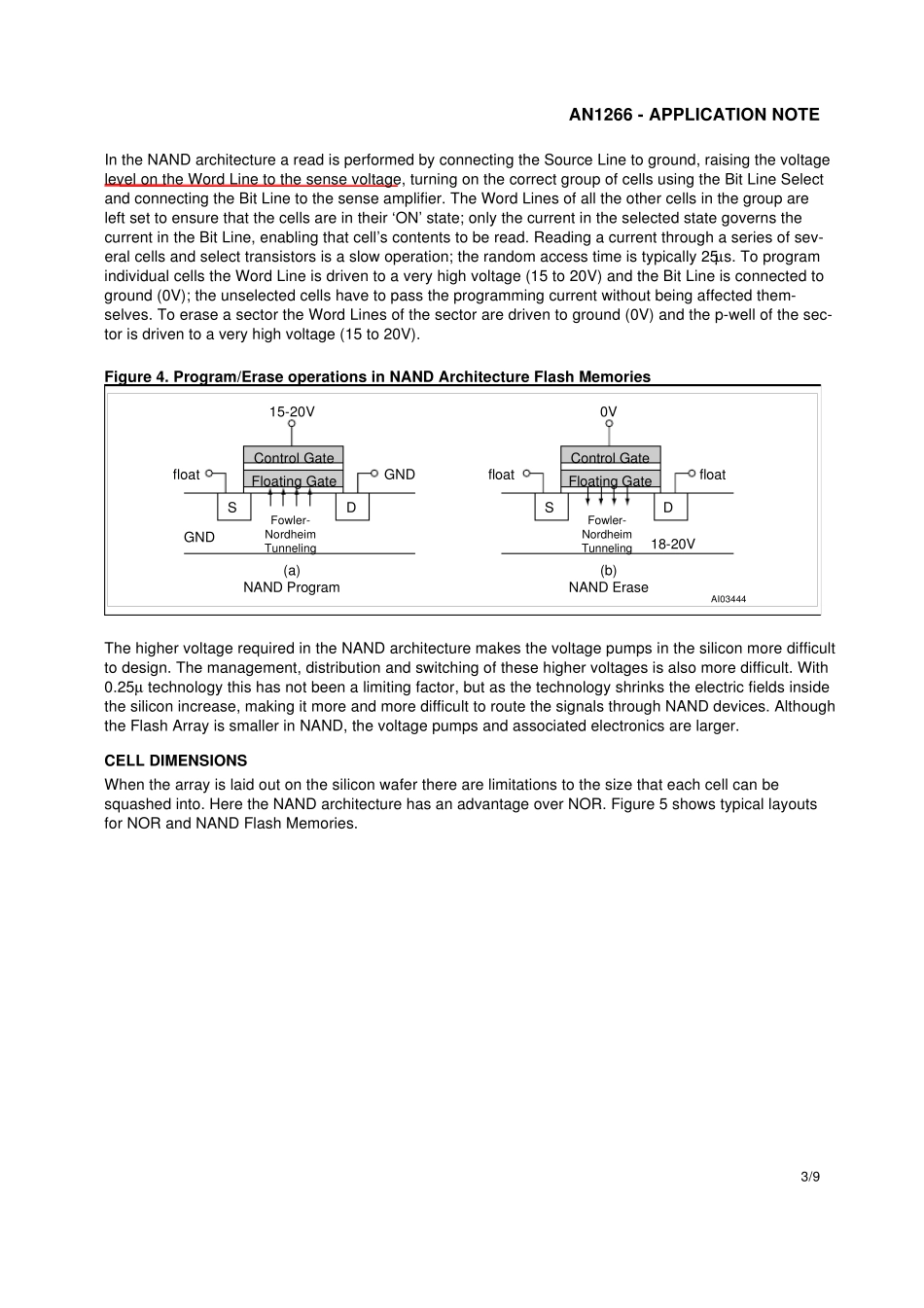
1/9March 2001AN1266APPLICATION NOTEBenchmarking Flash NOR and Flash NAND memoriesfor Code and Data StorageCONTENTSs INTRODUCTIONs CELL STRUCTUREs CELL DIMENSIONSs MULTI LEVEL CELLSs OPERATIONAL DIFFERENCESs COST TRENDSs CONCLUSIONs REFERENCESINTRODUCTIOMWhen choosing a Flash memory for a particular application it isimportant to know which type of Flash Memory is most suitable.There are now many manufacturers offering a wide range ofFlash Memories and users can be daunted by the prospect ofselecting the correct product for their application.This document aims to give a background on the underlyingtechnologies associated with Flash Memories. It will give thereader a clearer picture of which type of Flash Memory tochoose for their application. The advantages and disadvantag-es of each type of memory is discussed along with the under-lying principles that govern the properties of the memory.There are two fundamental Array Architecture that distinguishthe type of the Flash Memory, NOR and NAND. Although boththese types of memories can store large amounts of data, onlythe NOR type is suitable for fast random access required for ex-ecuting code directly from the Flash Memory, saving on shad-ow RAM costs.CELL STRUCTUREThe Basic Cell in a Flash Memory is a single MOS transistorbuilt with a Floating Gate between the control gate and the p-substrate. Figure 1 shows a typical cross section of the transis-tor.Figure 1. Cross section of the basic Flash Memory CellAI03431n+n+pSDCFloating GateSourceControl GateDrainSDCAN1266 - APPLICATION NOTE2/9The Floating Gate stores charge (electrons); the amount of charge on the gate determines whether theFlash Memory cell holds a value of ‘1’ or ‘0’. (In Multi-Bit Cells more than one bit ...