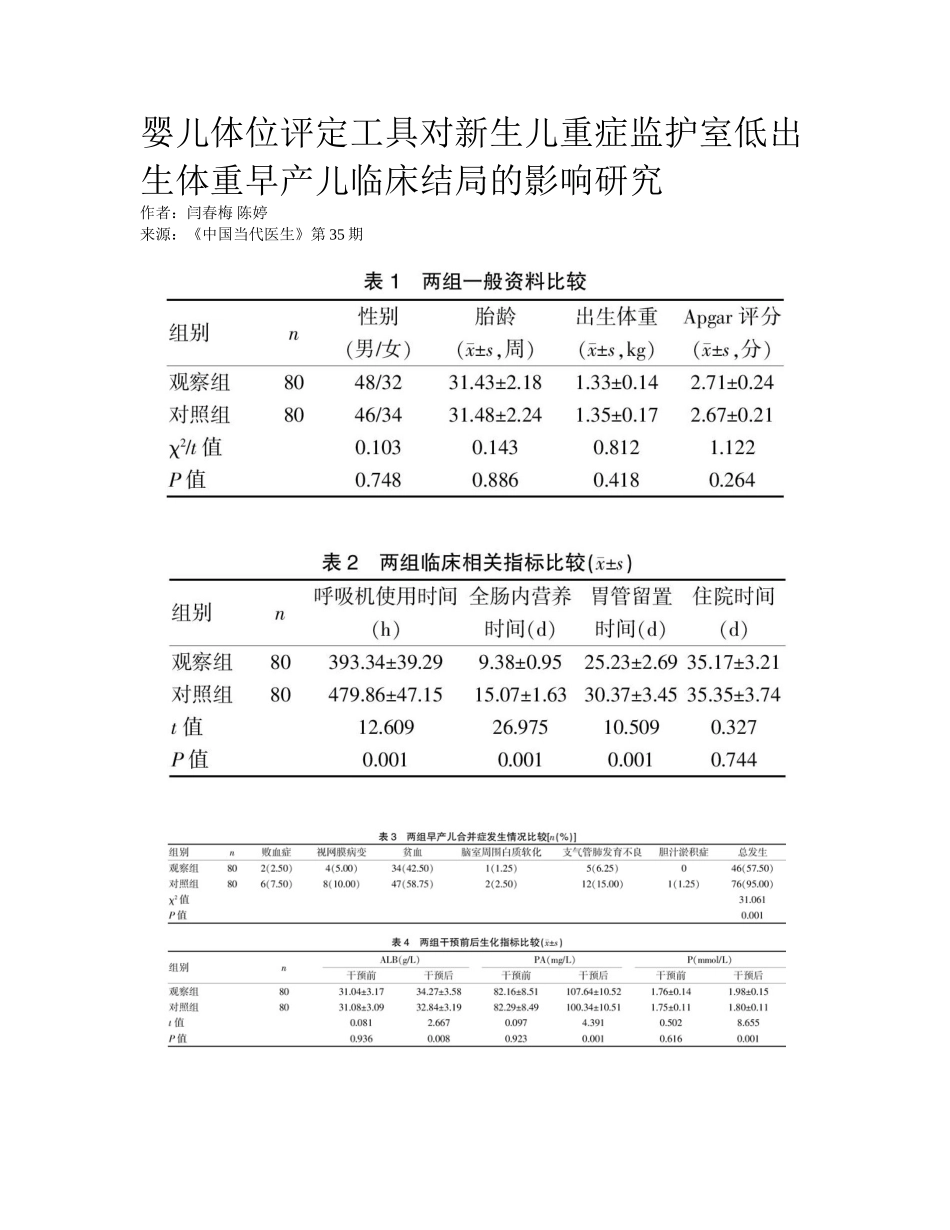
婴儿体位评定工具对新生儿重症监护室低出生体重早产儿临床结局的影响研究 作者:闫春梅 陈婷来源:《中国当代医生》第 35 期 [摘要] 目的 探討婴儿体位评定工具对新生儿重症监护室(NICU)低出生体重早产儿(LBWP )临床结局的影响研究。 办法 将我院 3 月~3 月收治的 80 例 NICU LBWP 患儿设为观察组,在鸟巢体位支持下,使用婴儿体位评定工具(IPAT)来指导摆位,另选用 1 月~1 月收治的 80 例 NICU LBWP 患儿设为对照组,予以鸟巢作为体位支持。比较两组患者临床有关指标(呼吸机使用时间、全肠内营养时间、胃管留置时间、住院时间)、早产儿合并症发生状况(败血症、视网膜病变、贫血、脑室周边白质软化、支气管肺发育不良、胆汁淤积症)及ALB、PA、P 等生化指标变化。 成果 两组住院时间比较,差别无统计学意义(P>0.05),与对照组相比,观察组在呼吸机使用时间、全肠内营养时间、胃管留置时间明显缩短(t=12.609、26.975、10.509,P0.05),干预后观察组 ALB、PA、P 均高于对照组,差别有统计学意义(t=2.667、4.391、8.655,P [核心词] 早产儿;婴儿体位评定工具;临床结局;新生儿重症监护室 [中图分类号] R71 [文献标记码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701()35-0051-04 [Abstract] Objective To investigate the impacts of infant posture assessment tool on the clinical outcome of low birth weight premature(LBWP ) infants in neonatal intensive care unit(NICU). Methods NICU LBWP infants admitted to our hospital from March to March were selected as the observation group(n=80 ), with the support of the bird's nest posture , the infant posture assessment tool(IPAT ) was used to guide the placement. Meanwhile , NICU LBWP infants admitted to our hospital from January to January were selected as the control group(n=80 ), with the support of the bird's nest posture. Clinical related indexes(ventilator use time , total enteral nutrition time , gastric tube indwelling time , hospitalization time ), complications of premature infants(septicemia , retinopathy , anemia , periventricul...