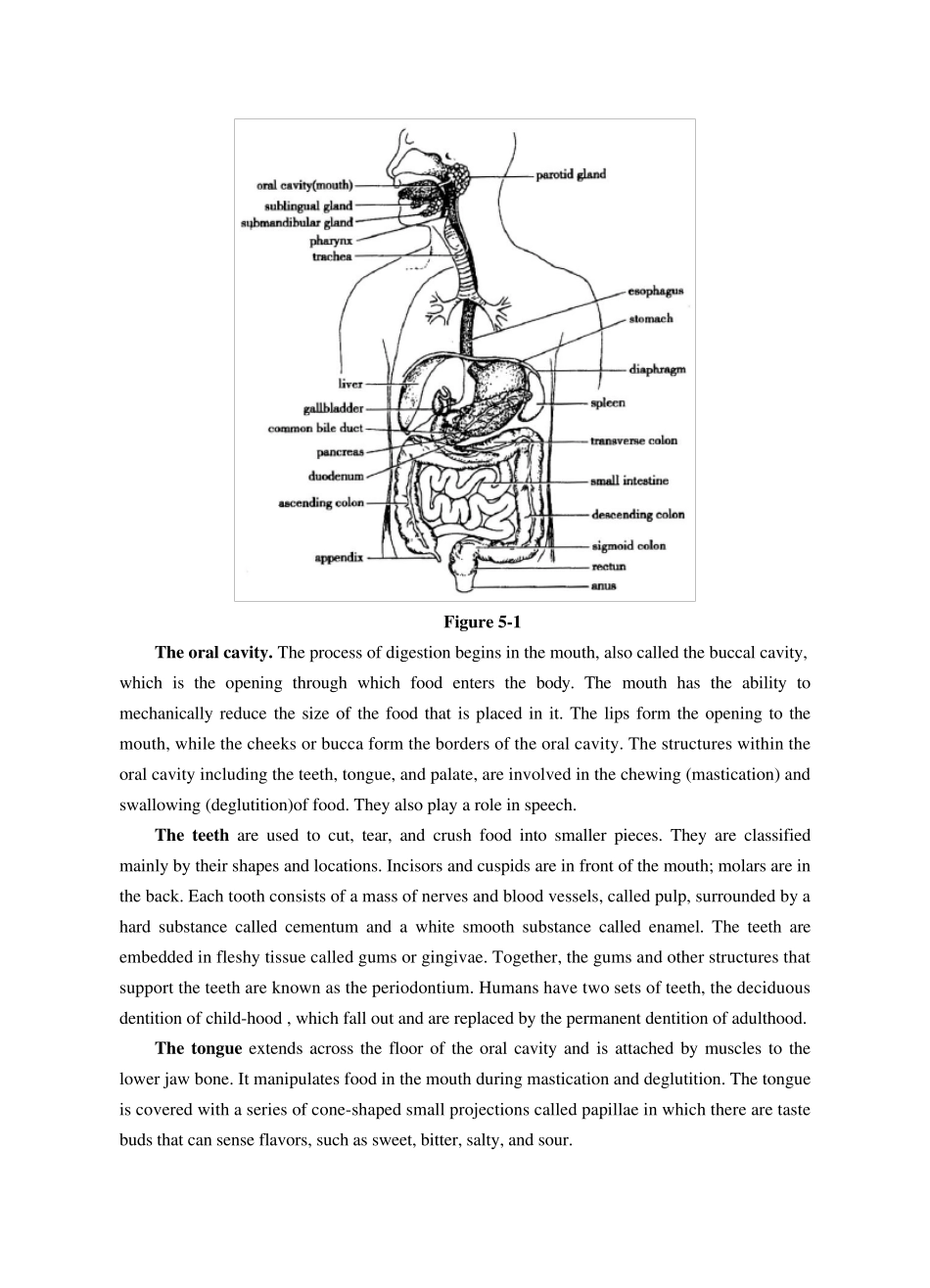
Chapter 4 The Digestiv e Sy stem In this passage you will learn: ● The digestive system as a whole ● Anatomy and physiology of the major organs in the digestive system ● Associated medical terms Introduction. The digestive system, also called the gastrointestinal or alimentary canal, contains the organs involved in the ingestion and processing of food. The primary functions of the digestive system are: ingestion—the entry of food into the body ; digestion—the physical and chemical breakdown of food into nutrients that can be used by the body's cells; absorption—the passage of these nutrients from the gastrointestinal tract into the bloodstream; and elimination—the excretion of solid waste materials that cannot be absorbed into the blood. Anatomy and Physiology. Anatomically, the digestive system consists of a 30-foot long, mucous membrane-lined tube beginning with the mouth, where food enters the body, and ending with the anus, where solid waste is excreted. The digestive system is composed of 9 main organs: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder and pancreas. The liver, gallbladder, and pancreas are also called accessory organs of the digestive system. Although food does not pass through these organs, they aid in the processing of food and nutrients. The organs of the digestive system are illustrated in Figure 5-1 and described in the paragraphs below. Figure 5-1 The oral cavity. The process of digestion begins in the mouth, also called the buccal cavity, which is the opening through which food enters the body. The mouth has the ability to mechanically reduce the size of the food that is placed in it. The lips form the opening to the mout...