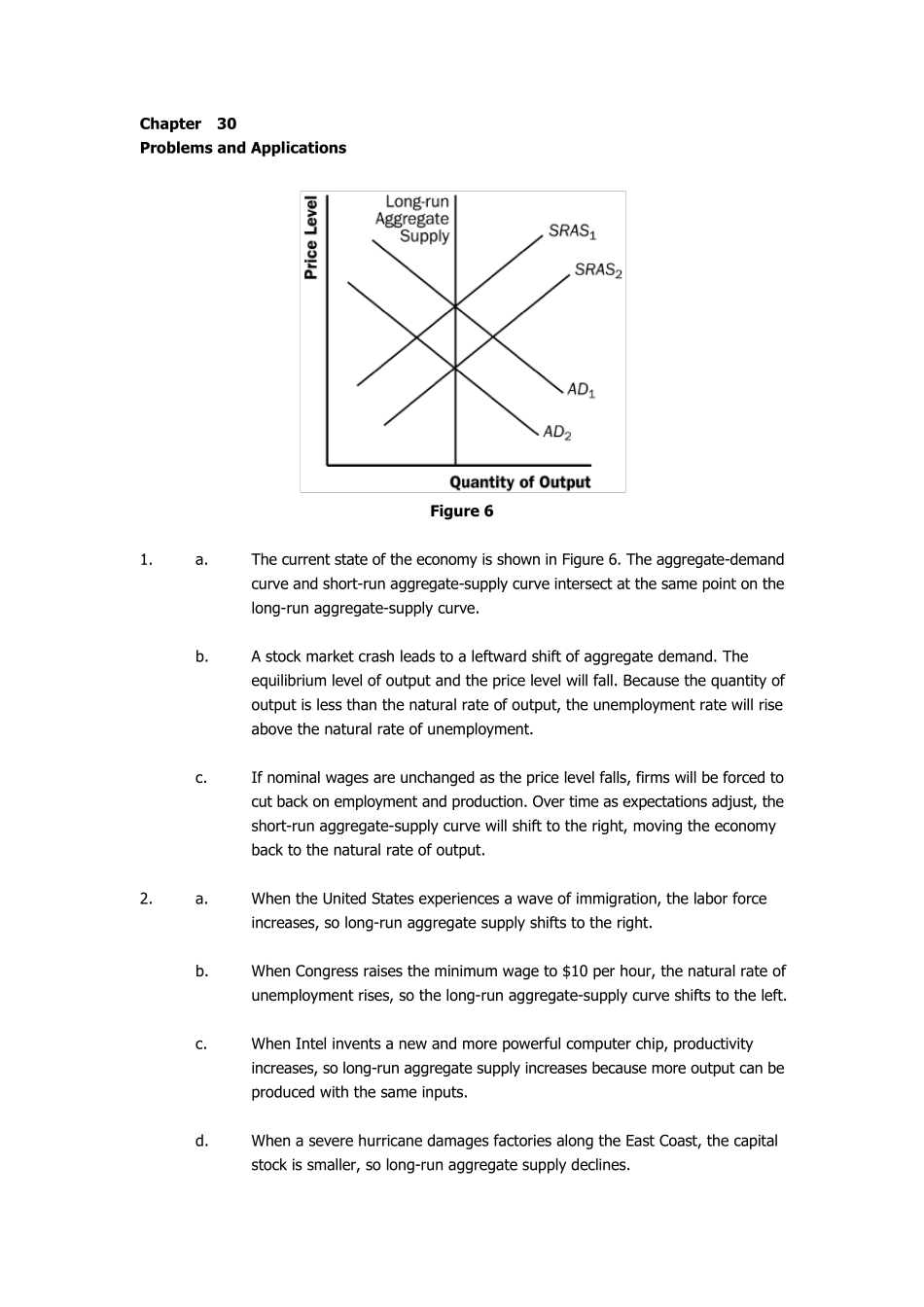
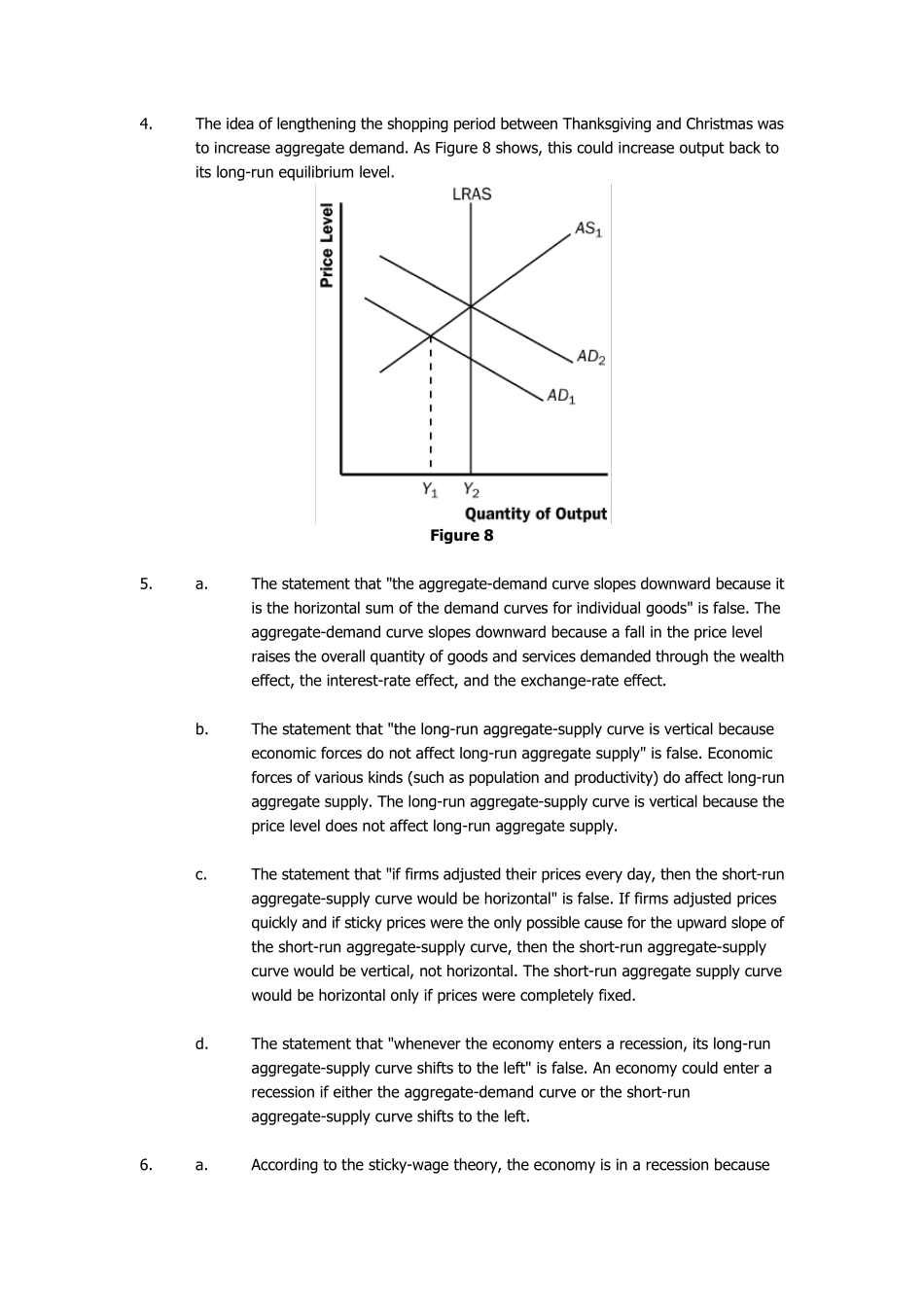
Chapter 30 Problems and Applications Figu re 6 1. a. The current state of the economy is shown in Figure 6. The aggregate-demand curve and short-run aggregate-supply curve intersect at the same point on the long-run aggregate-supply curve. b. A stock market crash leads to a leftward shift of aggregate demand. The equilibrium level of output and the price level will fall. Because the quantity of output is less than the natural rate of output, the unemployment rate will rise above the natural rate of unemployment. c. If nominal wages are unchanged as the price level falls, firms will be forced to cut back on employment and production. Over time as expectations adjust, the short-run aggregate-supply curve will shift to the right, moving the economy back to the natural rate of output. 2. a. When the United States experiences a wave of immigration, the labor force increases, so long-run aggregate supply shifts to the right. b. When Congress raises the minimum wage to $10 per hour, the natural rate of unemployment rises, so the long-run aggregate-supply curve shifts to the left. c. When Intel invents a new and more powerful computer chip, productivity increases, so long-run aggregate supply increases because more output can be produced with the same inputs. d. When a severe hurricane damages factories along the East Coast, the capital stock is smaller, so long-run aggregate supply declines. 3. a. The current state of the economy is shown in Figure 7. The aggregate-demand curve and short-run aggregate-supply curve intersect at the same point on the long-run aggregate-supply curve. Figu re 7 b. If the central bank increases the money supply, aggregate demand shifts to the right (to point B). In...