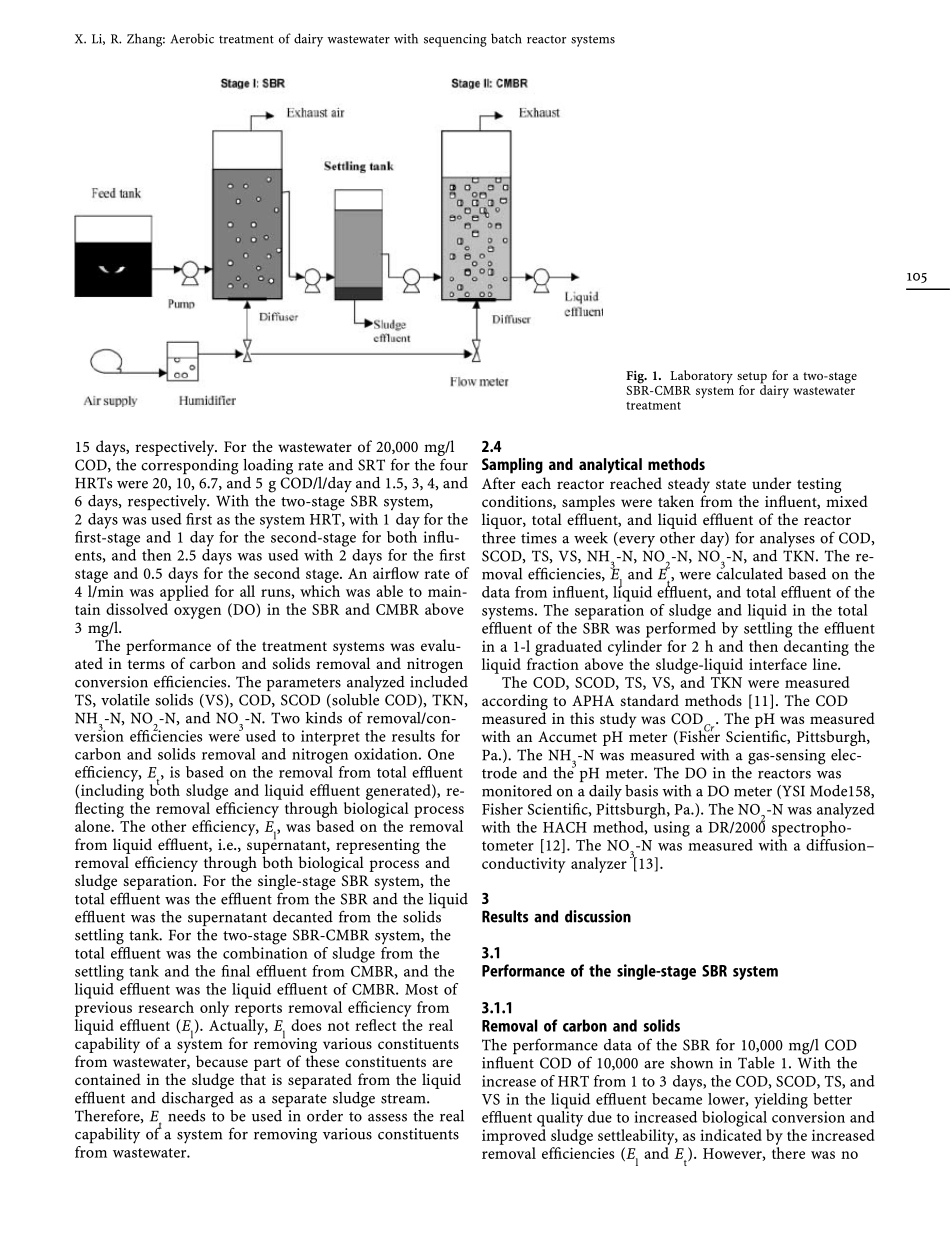
Aerobic treatment of dairywastewater with sequencingbatch reactor systemsXiu jin Li, Ru ihong ZhangAbstract Performances of single-stage and two-stage se-quencing batch reactor (SBR) systems were investigatedfor treating dairy wastewater. A single-stage SBR systemwas tested with 10,000 mg/l chemical oxygen demand(COD) influent at three hydraulic retention times (HRTs)of 1, 2, and 3 days and 20,000 mg/l COD influent at fourHRTs of 1, 2, 3, and 4 days. A 1-day HRT was foundsufficient for treating 10,000-mg/l COD wastewater, withthe removal efficiency of 80.2% COD, 63.4% total solids,66.2% volatile solids, 75% total Kjeldahl nitrogen, and38.3% total nitrogen from the liquid effluent. Two-dayHRT was believed sufficient for treating 20,000-mg/l CODdairy wastewater if complete ammonia oxidation is notdesired. However, 4-day HRT needs to be used forachieving complete ammonia oxidation. A two-stage sys-tem consisting of an SBR and a complete-mix biofilm re-actor was capable of achieving complete ammoniaoxidation and comparable carbon, solids, and nitrogenremoval while using at least 1/3 less HRT as compared tothe single SBR system.KeywordsAerobic, dairy, wastewater, sequencingbatch reactor1Introdu ctionDairy wastewater is currently disposed of mainly throughland application with little or no pretreatment in Califor-nia in the United States. Due to increasing awareness ofthe general public about potential adverse impact of ani-mal wastes on environmental quality and recent develop-ments in environmental regulations for gaseous-emissioncontrol and nutrient management, alternative wastewatertreatment methods become attractive options for dairyproducers. A sequencing batch reactor (SBR) is a biolog-ical treatment reactor that uses aerobic bacteri...