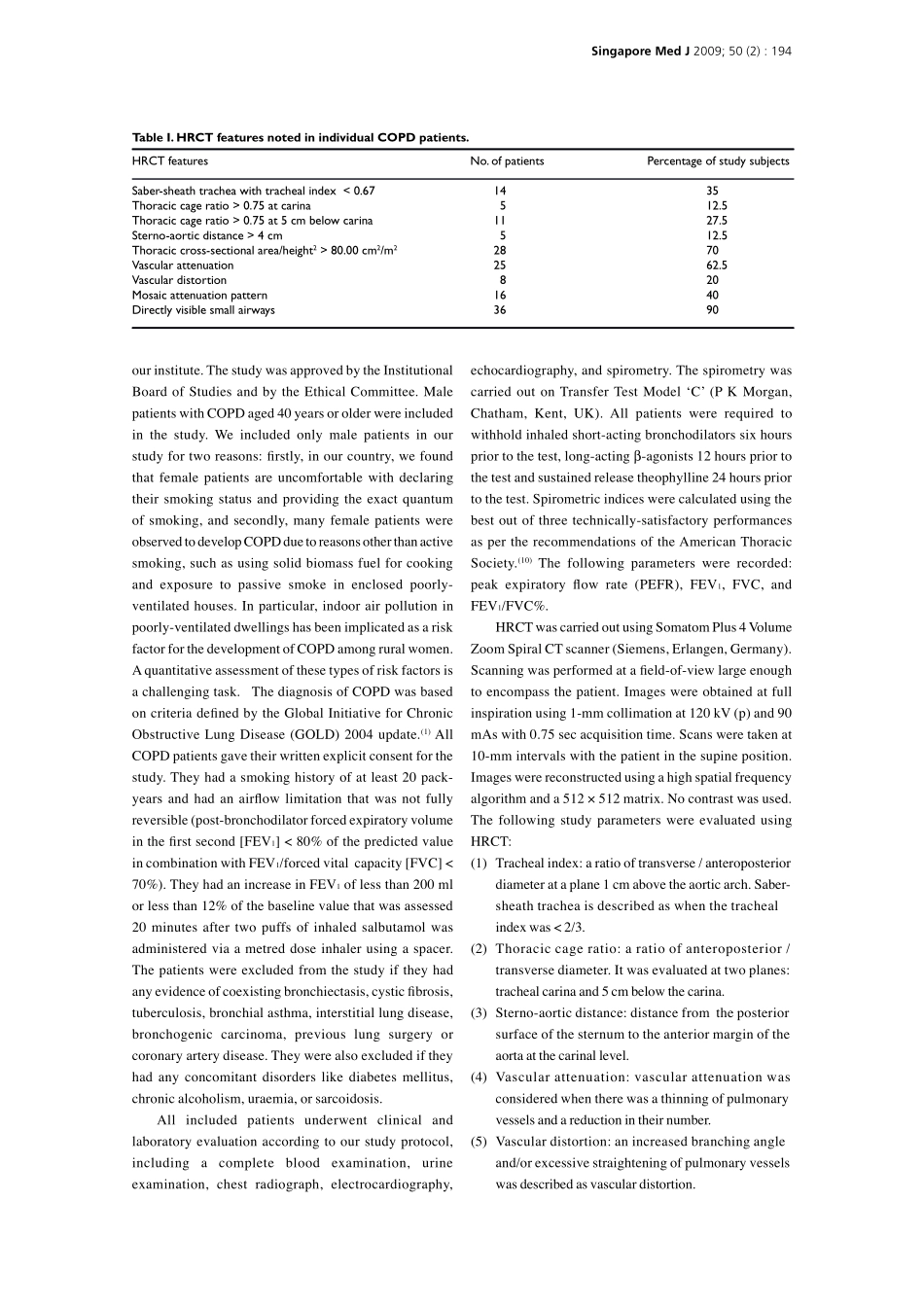
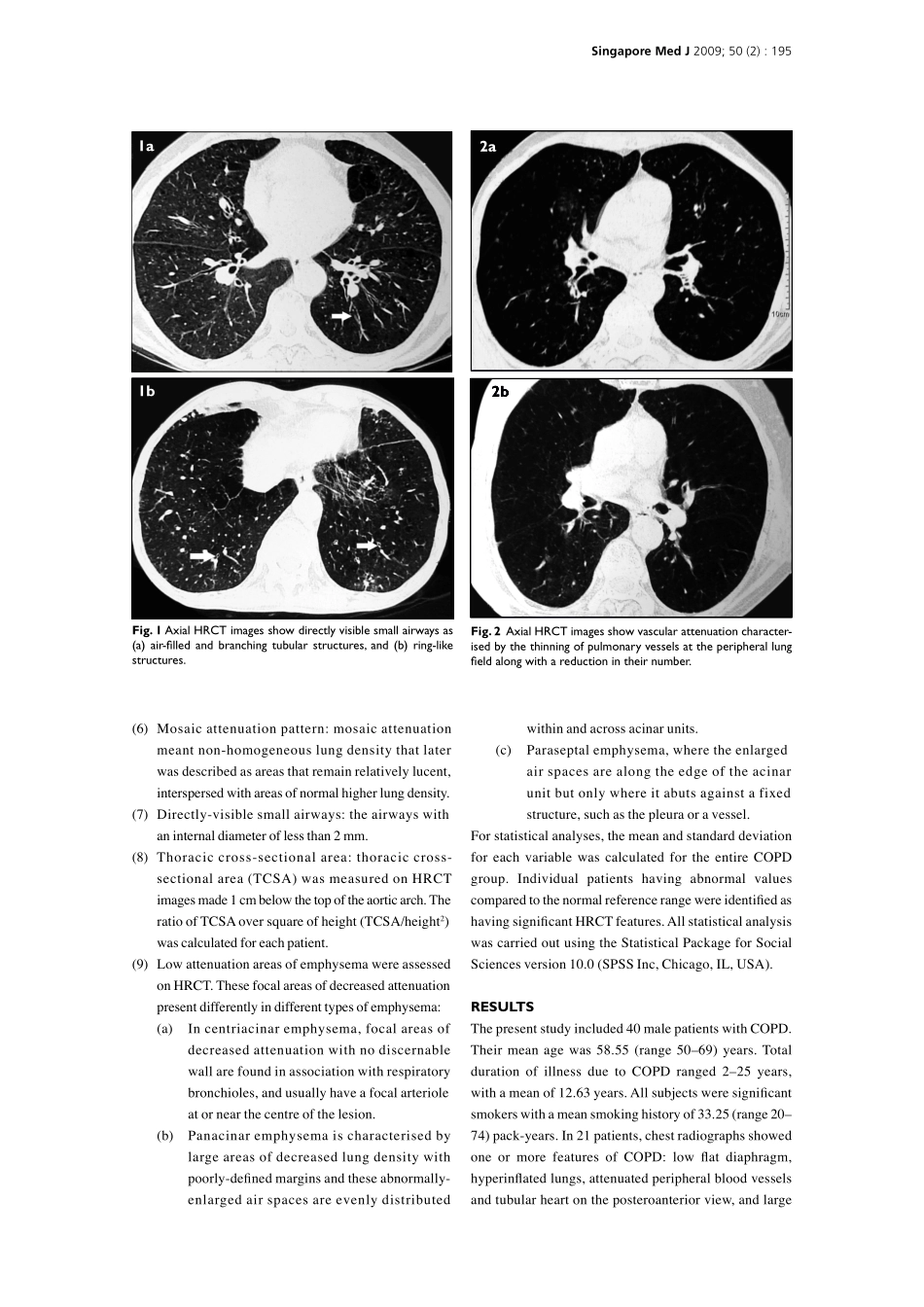
SingaporeMedJ2009;50(2):193OriginalArticleDepartmentofRespiratoryMedicine,PostgraduateInstituteofMedicalSciences,9J/17MedicalEnclave,Rohtak124001,IndiaGuptaPP,MD,FNCCP,FICAAIProfessorandChief,COPDClinicVermaM,MBBS,MDEx-ResidentGuptaKB,MDSeniorProfessorDepartmentofRadiodiagnosisYadavR,MDSeniorProfessorDepartmentofPhysiologyAgarwalD,MDAssistantProfessorCorrespondenceto:DrPremParkashGuptaTel:(91)1262212666Fax:(91)1262212666Email:gparkas@yahoo.co.inHigh-resolutioncomputedtomographyfeaturesinpatientswithchronicobstructivepulmonarydiseaseGuptaPP,YadavR,VermaM,GuptaKB,AgarwalDABSTRACTIntroduction:Inrecentyears,therehasbeenincreasinginterestindiagnosingvariouscomponentsofchronicobstructivepulmonarydisease(COPD)usinghigh-resolutioncomputedtomography(HRCT).ThepresentstudywasundertakentoevaluateHRCTfeaturesinpatientswithCOPD.Methods:40malepatientswithCOPD(age40yearsorolder)andwithasignificantsmokinghistory(20pack-yearsormore)wereincludedinthestudy.TheywereevaluatedforHRCTfeaturesincludingvascularattenuationanddistortion,mosaicattenuationpattern,directlyvisiblesmallairways,lowattenuationareasofemphysemaandmeasuresofhyperinflationofthelungs:trachealindex,sterno-aorticdistance,thoraciccageratioandthoraciccross-sectionalarea.Results:Thetrachealindexrangedfrom0.46to0.94;Saber-sheathtracheawasfoundin14patients.Themeanthoraciccageratioattwolevels,carinaand5cmbelowcarina,were0.69(range0.61–0.78)and0.73(range0.62–0.83),respectively.Sterno-aorticdistanceatcarinallevelrangedfrom1.43to4.55cm,withameanof3.00cm.Directlyvisiblesmallairwayswasthecommonestfinding(36patients),followedbyvascularattenuation(25patients),mosaicattenuationpattern(16patients)andvasculardistortion(8patients).Amongvarioussubtypesofemphysema,centriacinaremphysemawascommonest(16patients),followedbyparaseptal(13)andpanacinaremphysema(11).Conclusion:TherearecertainspecificHRCTfeaturesofemphysemaanditispossibleonHRCTtoidentifythesubtypesofemphysema,suchascentriacinar,panacinarandparaseptalemphysema.VariousfeaturesofhyperinflationcanalsobewellidentifiedandquantifiedonHRCT.Keywords:chronicbronchitis,chronicobstructivepulmonarydisease,emphysema,high-resolutioncomputedtomographySingaporeMedJ2009;50(2):193-200INTRODUCTIONChronicobstructivepulmonarydisease(COPD)isadiseasestatecharacterisedbyanairflowlimitationthatisnotfullyreversible.Theairflowlimitationisusuallybothprogressiveandassociatedwithanabnormalinflammatoryresponseofthelungstonoxiousparticlesorgases.(1)VariousdisordersincorporatedunderCOPDincludeemphysema,peripheralairwaysdiseaseandchronicbronchitis.Asthedefinitionofemphysemaisapathologicalone,itrequireshistopathologicalexaminationtoauthenticatethedisease,whichisnotusuallycarriedoutandoftennotconsentedtobythepatient.Moreover,duringtheearlystagesofCOPD,conventionalspirometrydoesnotrevealanyabnormalityastheearliestchangesinthesepatientsinvolvealveolarwallsandsmallairways,andamodestincreaseinperipheralairwaysresistanceisnotreflectedinsuchspirometricmeasurements.(2)Duringthelastfewdecades,withtheadventofhigh-resolutioncomputedtomography(HRCT),therehasbeenincreasedinterestindiagnosingemphysematousandchronicbronchitiscomponentsofCOPDusingHRCT.ManystudieshaveassessedHRCTfeaturesinpatientswithCOPD,(3-9)buttherewasaproblemwithnon-uniformityregardingtheincludedCOPDpatientpopulation,andthevariousstudieshaveevaluatedfordifferentHRCTfe...