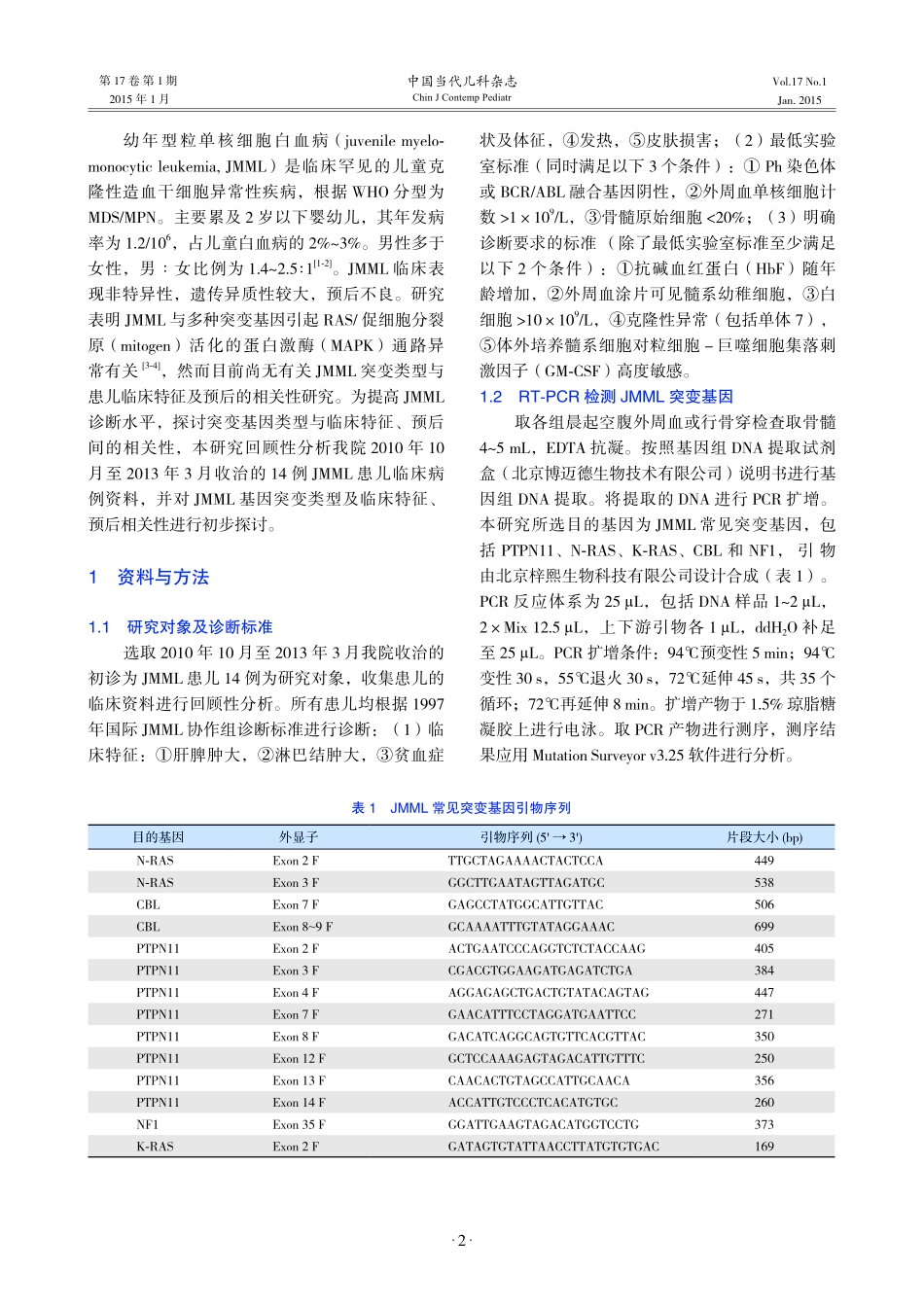
第17卷第1期2015年1月中国当代儿科杂志ChinJContempPediatrVol.17No.1Jan.2015·1·儿童幼年型粒单核细胞白血病突变基因型与临床特征分析杨文钰陈晓娟王书春郭晔刘天峰常丽贤刘芳竺晓凡(中国医学科学院血液病医院/血液学研究所儿童血液病诊疗中心,天津300020)[摘要]目的探讨儿童幼年型粒单核细胞白血病(JMML)突变基因类型及其临床特征。方法回顾性分析临床诊断明确且完成JMML常见突变基因检测的14例患儿临床资料。结果14例JMML患儿中,男11例(79%),女3例(21%)。诊断时中位年龄2.0岁(范围0.6~6.0岁)。14例患儿中检出PTPN11基因突变4例(29%),N-RAS基因突变3例(21%),1例同时伴有PTPN11和K-RAS基因突变(7%),6例未检测到突变基因(43%)。4例PTPN11基因突变患儿均为男性,中位发病年龄2.5岁,从发病至明确诊断中位时间为1.0个月,外周血WBC计数及单核细胞绝对值明显增高,PLT计数降低,随访至今3例患儿死亡,1例病情进展;3例N-RAS基因突变患儿男女比例为2:1,中位发病年龄2.0岁,从发病至明确诊断中位时间13.7个月,随访至今2例患儿死亡,1例未见明显进展。结论PTPN11是JMML最常见的突变基因类型,常伴有血WBC计数及单核细胞绝对值增高,PLT计数降低,疾病进展迅速,预后不良;N-RAS突变病例病情进展缓慢;复合突变基因类型由于病例数少,临床特征有待于临床进一步观察。[中国当代儿科杂志,2015,17(1):1-5][关键词]幼年型粒单核细胞白血病;突变基因;临床特征;儿童GenemutationsandclinicalcharacteristicsinchildrenwithjuvenilemyelomonocyticleukemiaYANGWen-Yu,CHENXiao-Juan,WANGShu-Chun,GUOYe,LIUTian-Feng,CHANGLi-Xian,LIUFang,ZHUXiao-Fan.DiagnosticandTherapeuticCenterofChildren'sBloodDisease,InstituteofHematology,BloodDiseaseHospital,ChineseAcademyofMedicalScience,Tianjin300020,China(ZhuX-F,Email:xfzhu1981@126.com)Abstract:ObjectiveTostudygenemutationsandclinicalfeaturesinchildrenwithjuvenilemyelomonocyticleukemia(JMML).MethodsTheclinicaldataof14childrenwhowerediagnosedwithJMMLandwereexaminedforthedetectionofcommongenemutationswereretrospectivelyanalyzed.ResultsEleven(79%)outof14casesweremale,and3(21%)werefemale.Themedianageatdiagnosiswas2.0years(agerange:0.6-6.0years).Among14cases,therewere4cases(29%)withPTPN11mutation,3cases(21%)withN-RASmutation,1case(7%)withPTPN11mutationandK-RASmutation,and6cases(43%)withoutanymutation.AllfourcasesinthePTPN11mutationgroupweremale,andtheirmedianagewas2.5years;intervalfromonsettodiagnosiswas1.0month;thewhitebloodcell(WBC)countandabsolutemonocytesinperipheralbloodweresignificantlyhigher,whiletheplatelet(PLT)countwaslower,ascomparedwiththeotherthreegroups;theywerefollowedup,and3casesdiedand1casehadaprogressivedisease.IntheN-RASmutationgroup,thereweretwomalecasesandonefemalecase,andtheirmedianagewas2.0years;intervalfromonsettodiagnosiswas13.7months;afterfollow-up,2casesdiedand1casedidnothaveanobviouslyprogressivedisease.ConclusionsPTPN11mutationisthemostcommonmutationinJMML.ThecaseswithPTPN11mutationoftenhavehigherWBCcountandabsolutemonocytesinperipheralblood,alowerPLTcount,andarapiddiseaseprogression,andtheirclinicaloutcomesarepoor.ThecaseswithN-RASmutationhaveaslowdiseaseprogression.Theclinicalcharacteristicsofthepatientswithcompoundmutationsarenotsurebecauseofthesmallnumberofcases,andfurtherclinicalobservationisindispensable.[ChinJContempPediatr,2015,17(1):1-5]Keywords:Juvenilemyelomonocyticleukemia;Genemutation;Clinicalcharacteristics;Child论著·临床研究[收稿日期]2014-06-03;[接受日期]2014-09-04[基金项目]国家自然科学基金(81300393,81300394)。[作者简介]杨文钰,女,博士,副主任医师。[通信作者]竺晓凡,女,...