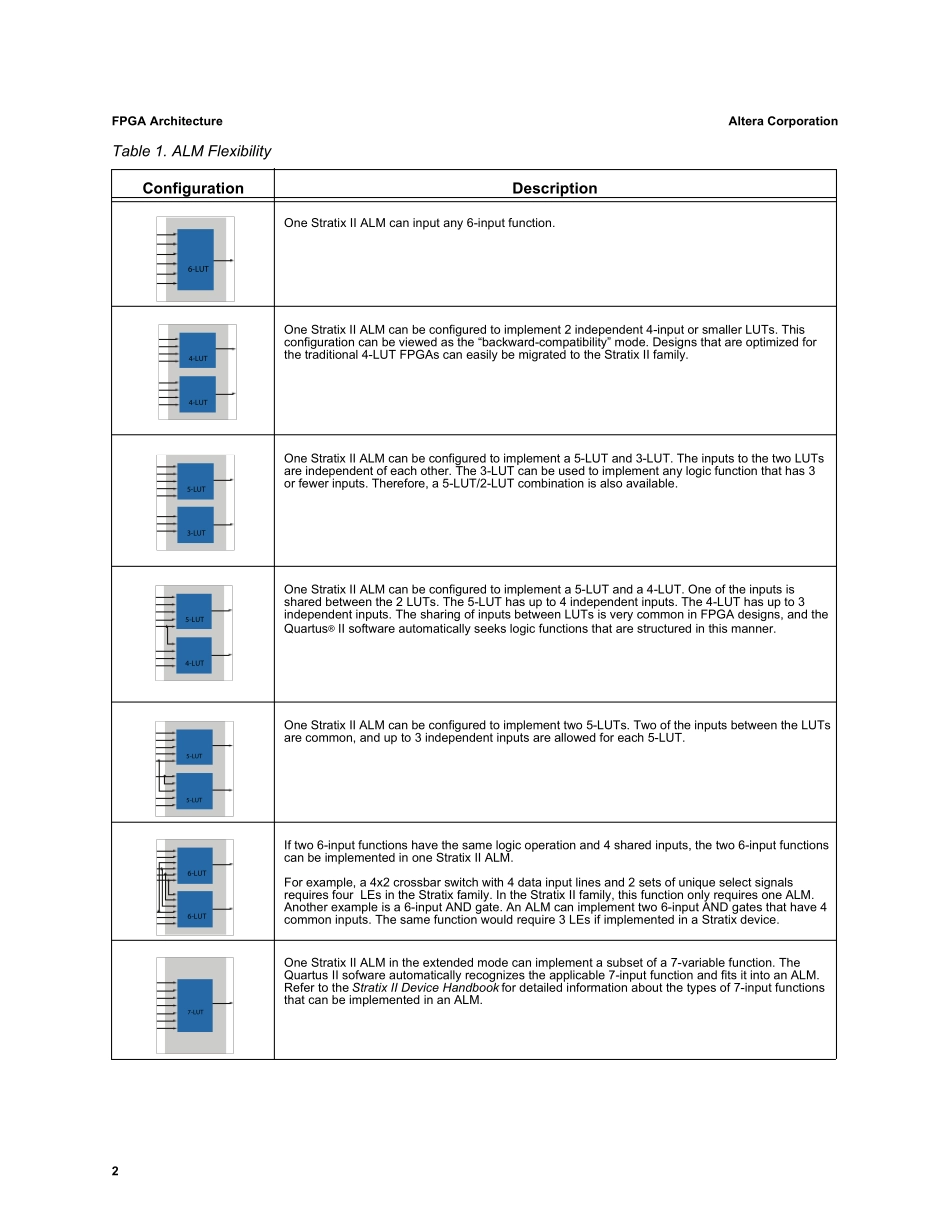
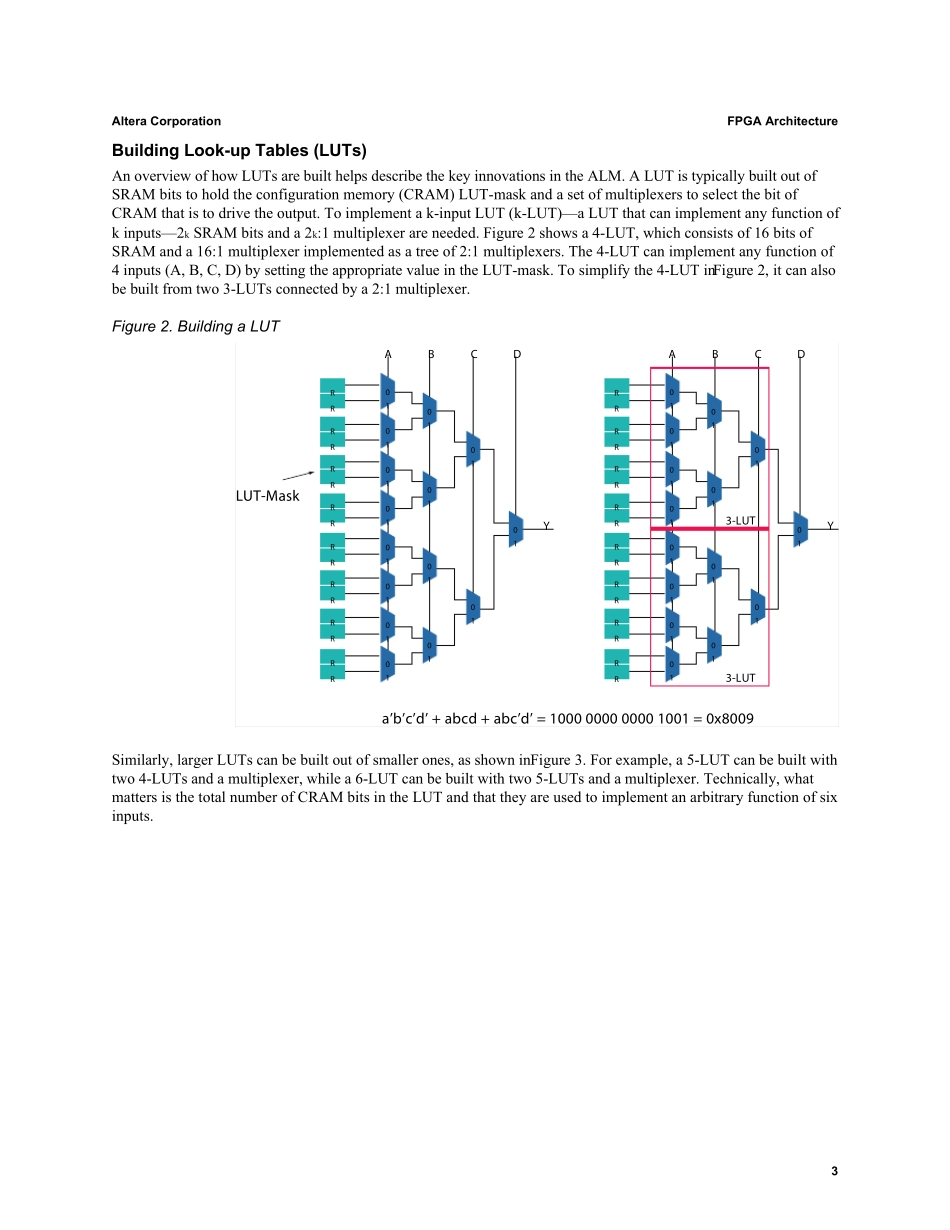
White PaperFPGA ArchitectureJuly 2006, ver. 1.01W P-01003-1.0IntroductionAltera continues to lead the FPGA industry in architectural innovation. The logic fabric and routing architecture in Altera® FPGAs are unmatched, providing customers with a number of advantages. Altera was the first to introduce the 8-input fracturable look-up table (LUT) with the Stratix® II family in 2004. At its core is the adaptive logic module (ALM) with 8 inputs, which can implement a full 6-input LUT (6-LUT) or select 7-input functions. The ALM can also be efficiently partitioned into independent smaller LUTs, providing the performance advantage of larger LUTs and the area efficiency of smaller LUTs. The Stratix series of FPGAs also excels in routing through the MultiTrack™ interconnect, which provides the industry’s best connectivity. As a result, Altera FPGA architecture is at least one generation ahead of the competition, and routing architecture is two generations ahead. This paper describes the leading-edge architectural innovations in Altera FPGAs and their advantages:■The ALM’s 1.8X density advantage over the competition■Optimal register-to-logic ratio (2:1) to ensure that the devices are not register-limited■The most routing connectivity, with up to five times the logic in a single hop compared to the competition Logic FabricThe key to the high-performance, area-efficient architecture is the ALM. It consists of combinational logic, two registers, and two adders as shown in Figure 1. The combinational portion has eight inputs and includes a LUT that can be divided between two adaptive LUTs (ALUTs) using Altera’s patented LUT technology. An entire ALM is needed to implement an arbitrary six-input function, but because i...