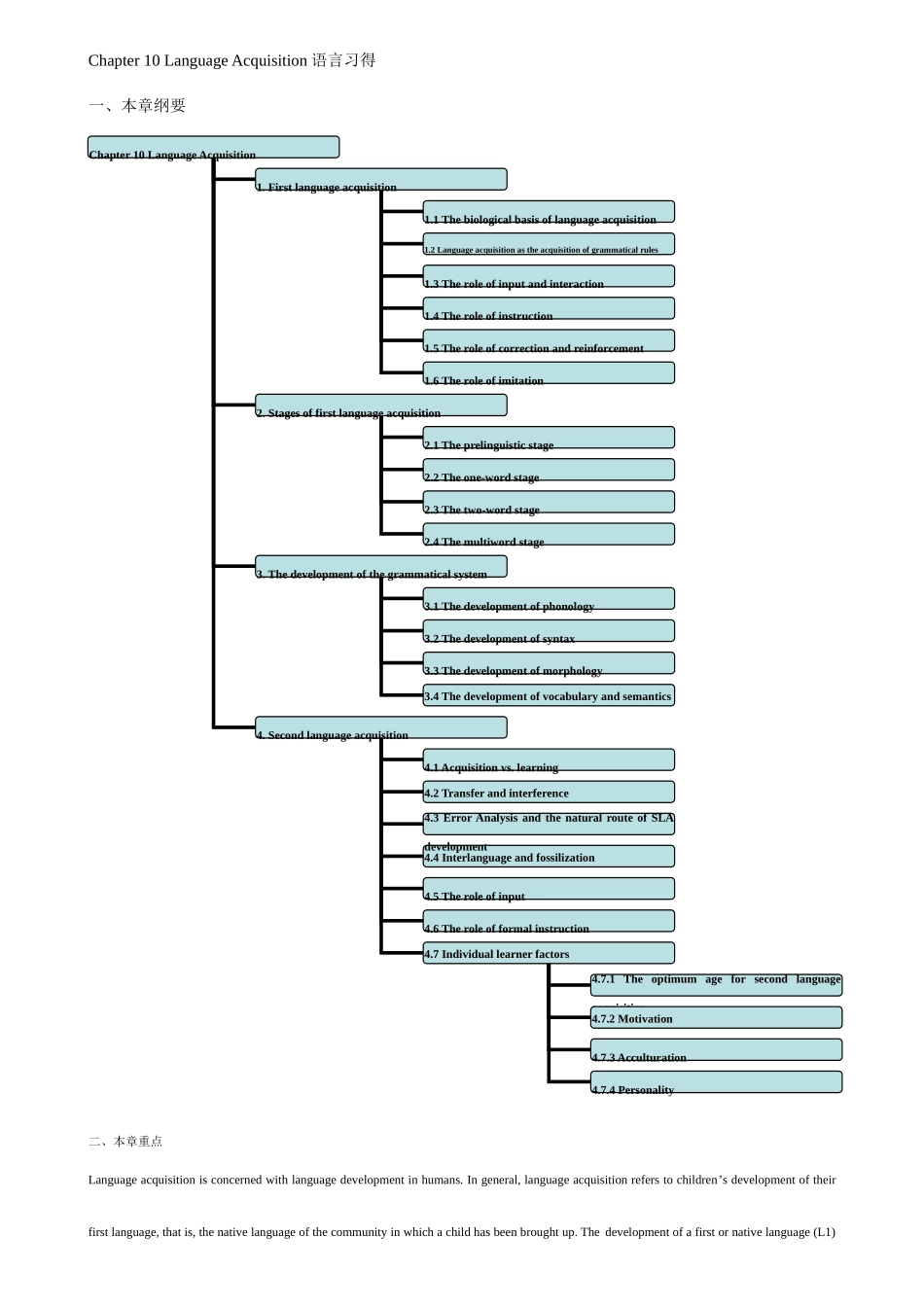
Chapter 10 Language Acquisition 语言习得一、本章纲要二、本章重点Language acquisition is concerned with language development in humans. In general, language acquisition refers to children’s development of their first language, that is, the native language of the community in which a child has been brought up. The development of a first or native language (L1) Chapter 10 Language Acquisition1. First language acquisition2. Stages of first language acquisition2.1 The prelinguistic stage 3. The development of the grammatical system4. Second language acquisition 3.1 The development of phonology 4.1 Acquisition vs. learning4.7 Individual learner factors 2.4 The multiword stage2.3 The two-word stage 2.2 The one-word stage1.1 The biological basis of language acquisition1.2 Language acquisition as the acquisition of grammatical rules1.3 The role of input and interaction1.4 The role of instruction1.5 The role of correction and reinforcement1.6 The role of imitation3.4 The development of vocabulary and semantics3.3 The development of morphology3.2 The development of syntax4.6 The role of formal instruction4.5 The role of input4.4 Interlanguage and fossilization 4.3 Error Analysis and the natural route of SLA development4.2 Transfer and interference4.7.1 The optimum age for second language acquisition4.7.2 Motivation4.7.3 Acculturation4.7.4 Personalityis called first language acquisition (FLA), and then second language acquisition (SLA). L1 and L2 development do not seem to involve identical processes. 语言习得关注旳是人类语言能力发展。语言习得一般指小朋友母语旳发展。有些孩子除了习得母语外,还要继续习得第二语言或外国语。习得母语或第一语言称为第一语言习得,除了母语再习得另一门语言或外语称为第二语言习得。The study of language acquisition enables linguists, psychologists...