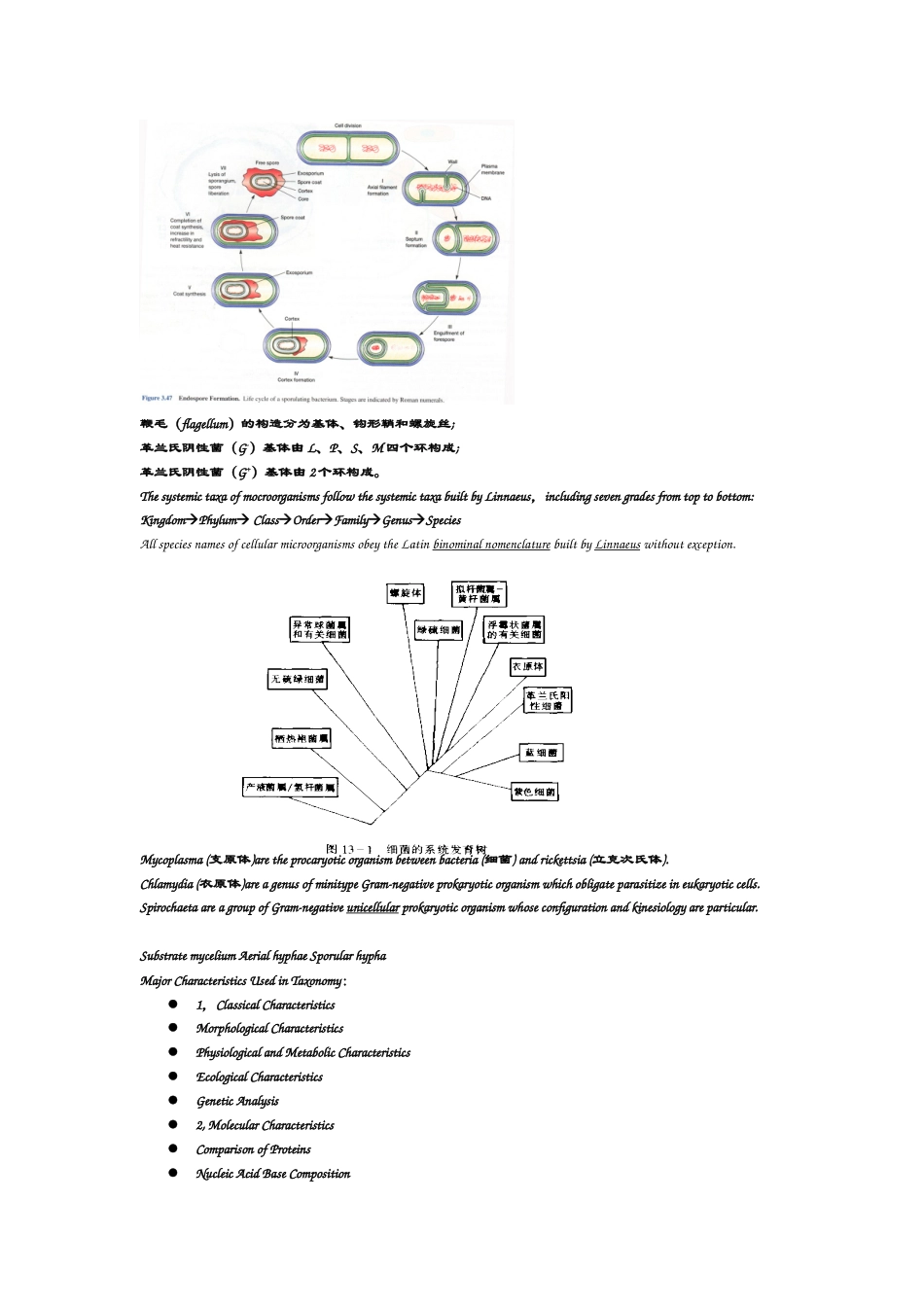
IntroductionMicrobes are a diverse group of organisms that can be divided into the viruses, unicellular groups (Archaea, Eubacteria, protista, some fungi and some chlorophyta) and a small number of organisms with a simple multicellular structure (the large fungi and chlorophyta).Microbiology: the science (logos) of small (micro) life (bios). The study of living things so small that they cannot be seen with the naked eye.The three-domain system is a biological classification introduced by Carl Woese that divides cellular life forms into archaea, bacteria, and eukaryote domains. In particular, it emphasizes the separation of prokaryotes into two groups, originally called Eubacteria (now Bacteria) and Archaebacteria (now Archaea).Microorganisms were first visualized by Antoni van Leeuwenhoek (1632–1723), a Dutch cloth merchant and an expert lens grinder.The first proof of the involvement of bacteria in disease and the definitive proof of the germ theory of disease came from the German Robert Koch.Koch’s postulates:1, The microorganism must be present in every instance of the disease and absent from healthy individuals.2, The microorganism must be capable of being isolated and grown in pure culture.3 ,When the microorganism is inoculated into a healthy host, the same disease condition must result.4, The same microorganism must be re-isolated from the experimentally infected host.Chapter oneFungi include yeasts, molds, and mushrooms.Viruses are noncellular organisms; they are intra-cellular parasites of animals, plants, or bacteria. 1, The Prokaryotes can be divided into two kingdoms, Bacteria and Archaea. The classification was first proposed by Woese based on the differences in 16S rRNA sequence.2, Prokaryotic microorga...