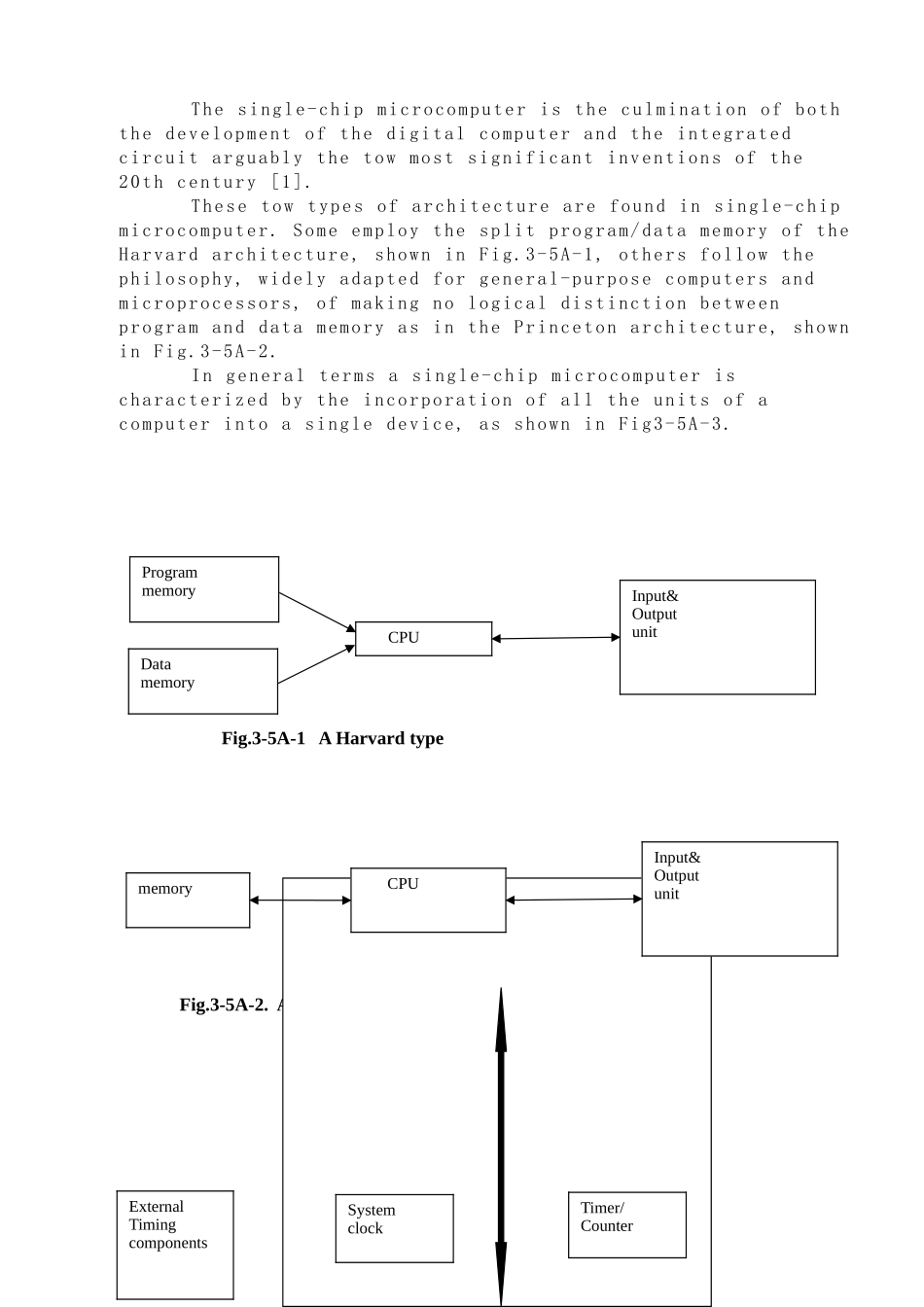
毕业设计(论文)外文资料翻译 系别: 电气系 专业: 电气工程及其自动化 附 件:1 、外文原文; 2 、外文资料翻译译文。 指导老师评语:签字: 年 月 日注:请将该封面与附件装订成册。1、 外文原文(复印件) A: Fundamentals of Single-chip Microcomputer The single-chip microcomputer is the culmination of both the development of the digital computer and the integrated circuit arguably the tow most significant inventions of the 20th century [1]. These tow types of architecture are found in single-chip microcomputer. Some employ the split program/data memory of the Harvard architecture, shown in Fig.3-5A-1, others follow the philosophy, widely adapted for general-purpose computers and microprocessors, of making no logical distinction between program and data memory as in the Princeton architecture, shown in Fig.3-5A-2. In general terms a single-chip microcomputer is characterized by the incorporation of all the units of a computer into a single device, as shown in Fig3-5A-3. Fig.3-5A-1 A Harvard type Fig.3-5A-2. A conventional Princeton computerProgrammemoryDatamemory CPUInput&Outputunitmemory CPUInput&OutputunitExternalTimingcomponentsSystemclockTimer/Counter Reset Interrupts Power Fig3-5A-3. Principal features of a microcomputer Read only memory (ROM).ROM is usually for the permanent, non-volatile storage of an applications program .Many microcomputers and microcontrollers are intended for high-volume applications and hence the economical manufacture of the devices requires that the contents of the program memory be committed permanently during the manufacture of chips . Clearly, this implies a rigorous approach to ROM code development since changes cannot be made after manufacture .This development process may involve emulation using a sophisticated developm...