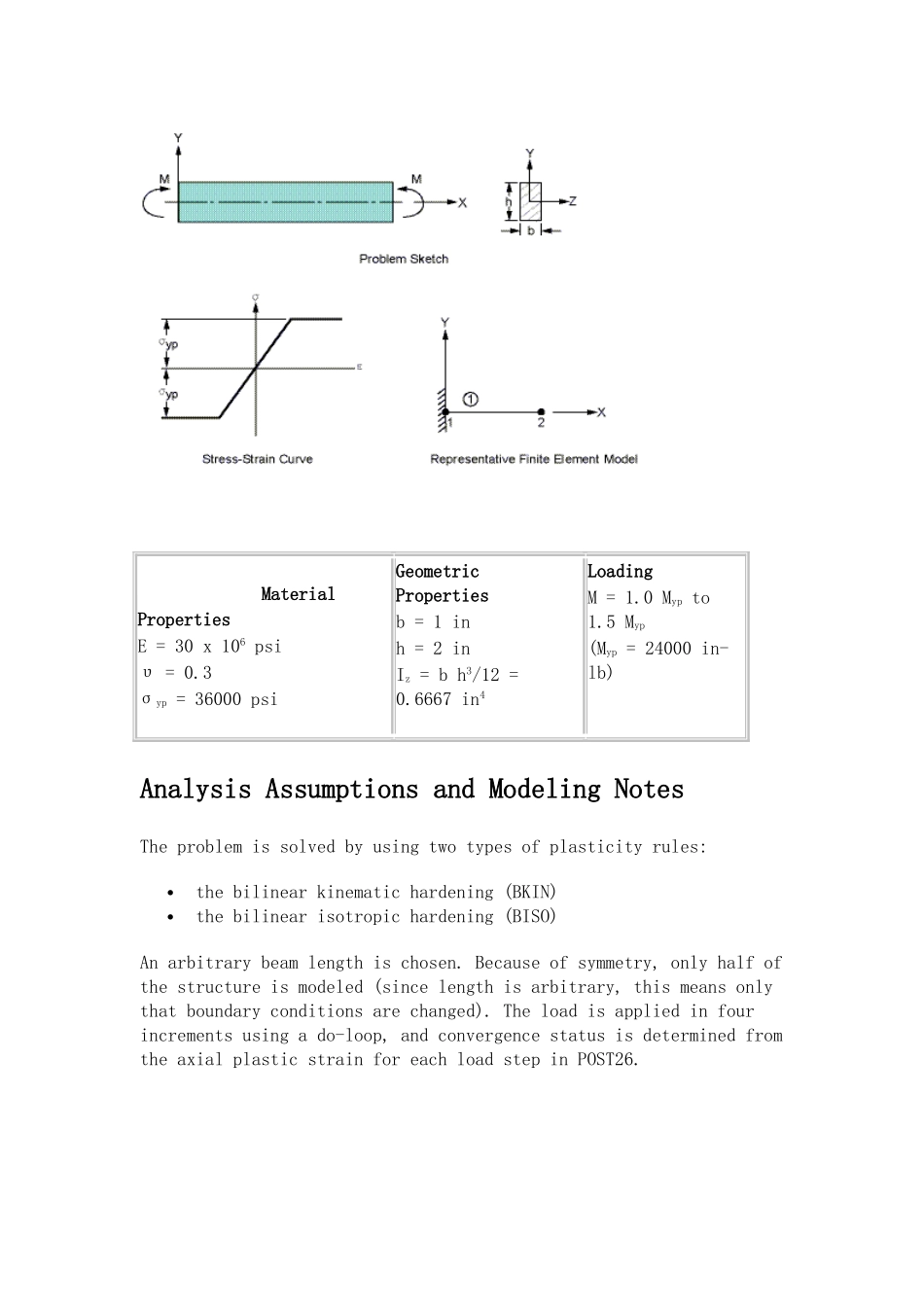
矩形梁的弹塑性分析(VM24)1 原附件1.1 帮助文档(VM24)VM24Plastic Hinge in a Rectangular BeamOverviewReference:S. Timoshenko, Strength of Material, Part II, Elementary Theory and Problems, 3rd Edition, D. Van Nostrand Co., Inc., New York, NY, 1956, pg. 349, article 64.Analysis Type(s):Static, Plastic Analysis (ANTYPE = 0)Element Type(s):2-D Plastic Beam Element (BEAM23)Input Listing:vm24 .dat Test CaseA rectangular beam is loaded in pure bending. For an elastic-perfectly-plastic stress-strain behavior, show that the beam remains elastic at M = Myp = σyp bh2/6 and becomes completely plastic at M = Mult = 1.5 Myp.Figure 24.1 Plastic Hinge Problem Sketch Material PropertiesE = 30 x 106 psiυ = 0.3σyp = 36000 psiGeometric Propertiesb = 1 inh = 2 inIz = b h3/12 = 0.6667 in4LoadingM = 1.0 Myp to 1.5 Myp(Myp = 24000 in-lb)Analysis Assumptions and Modeling NotesThe problem is solved by using two types of plasticity rules: the bilinear kinematic hardening (BKIN)the bilinear isotropic hardening (BISO)An arbitrary beam length is chosen. Because of symmetry, only half of the structure is modeled (since length is arbitrary, this means only that boundary conditions are changed). The load is applied in four increments using a do-loop, and convergence status is determined from the axial plastic strain for each load step in POST26.Results Comparison (for both analyses)M/MypTargetANSYSRatio1.0Fully ElasticFully Elastic--1.1666Elastic-PlasticElastic-Plastic[1]--1.3333Elastic-PlasticElastic-Plastic[1]--1.5Fully PlasticFully Plastic[2]--1. Solution converges2. Solution does not converge (indicates that the structure has collapsed). Moment ratios slightly less than 1.5 will also show a collapse since plasticity is monitored only at discrete integ...