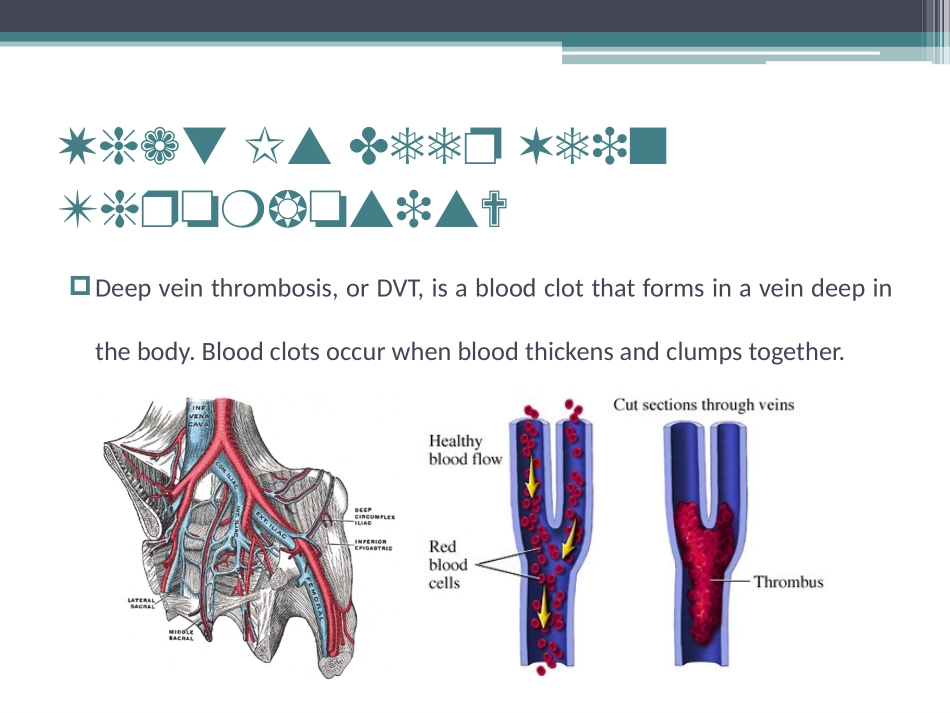
DeepveinthrombosisXiangYuChengWhatIsDeepVeinThrombosis?TheearliestcaseofDVTwasdescribedaround600-900BC.Atsomepoint,theincreasedincidenceofDVTinwomenafterchildbirthwasnoticed,andinthelate1700s,apublichealthrecommendationwasissuedtoencouragewomentobreastfeedasameanstopreventthisphenomenon;theDVTwascalled"milkleg",asitwasthoughttoresultfrommilkbuildingupintheleg.WhatIsDeepVeinThrombosis?Deepveinthrombosis,orDVT,isabloodclotthatformsinaveindeepinthebody.Bloodclotsoccurwhenbloodthickensandclumpstogether.WhatIsDeepVeinThrombosis?Abloodclotinadeepveincanbreakoffandtravelthroughtheblood.Theemboluscouldtraveltoanarteryinthelungsandblockbloodflow.Thisconditioniscalledpulmonaryembolism,orPE.EpidemiologyDeepveinthrombosis*DiagnosesofDVTandPEarenotmutuallyexclusive;anestimated78,511patientsreceiveddiagnosesofbothDVTandPE.VTEestimatesincludepatientswithdiagnosesofeitherDVTorPE.EpidemiologyDeepveinthrombosisAccordingtothemostrecentACCPguidelines,VTEremainsthesecondmostcommoncauseofprotractedhospitalstayandthethirdmostcommoncauseofexcessmortalityamong7millionpatientsdischargedfrom944acutecarehospitalsintheUS.CausesGermanpathologistRudolfVirchowpostulatedtheinterplayofthreeprocessesresultinginvenousthrombosis,nowknownasVirchow'striad:DeepveinthrombosisInkeepingwithVirchow'sconcept,alterationsofthecoagulationsystemthatinduceahypercoagulablestatealsoconferanincreasedriskofDVT.CausesGermanpathologistRudolfVirchowpostulatedtheinterplayofthreeprocessesresultinginvenousthrombosis,nowknownasVirchow'striad:DeepveinthrombosisCausesThebloodflowpatterninthevalvescancausehypoxemia,whichisworsenedbyvenousstasis,activatespathways-onesthatincludehypoxia-induciblefactor-1andearly-growth-responseprotein1.Hypoxia-induciblefactor-1andearly-growth-responseprotein1contributetomonocyteassociationwithendothelialproteins,suchasP-selectin,promptingmonocytestoreleasetissuefactor-filledmicrovesicles,whichpresumablybeginclottingafterbindingtotheendothelialsurface.[9]DeepveinthrombosisCausesIndependentRiskFactorsforDVTAgeisanindependentriskfactorforthromboticdisease.Themajorityofvenousthrombioccurineitherthesuperficialordeepveinsoftheleg.ADVTisstationaryclottingbloodadheredtothedeepveinofthepelvisoranextremityandusuallyoccursinthecalforthigh.VTEdenotesanobstructionarisingfromtheformationofaclotinthevenouscirculationcarriedbythebloodfromthesiteoforigintopluganothervessel.DeepveinthrombosisCausesIndependentRiskFactorsforDVTDeepveinthrombosisSignsandsymptomsCommonsignsandsymptomsofDVTinclude:√Pain…√Swelling…√Warmth…√Rednessordiscoloration…√Distentionofsurfaceveins…DeepveinthrombosisSignsandsymptomsCommonsignsandsymptomsofDVTinclude:√Pain…√Swelling…√Warmth…√Rednessordiscoloration…√Distentionofsurfaceveins…DeepveinthrombosisSignsandsymptomsInmostsuspectedcases,DVTisruledoutafterevaluation,andsymptomsaremoreoftenduetoothercauses,suchascellulitis,Baker'scyst,musculoskeletalinjury,orlymphedema.Otherdifferentialdiagnosesincludehematoma,tumors,venousorarterialaneurysms,andconnectivetissuedisorders.DeepveinthrombosisDiagnosisProbability:InthosewithsuspectedDVT,aclinicalassessmentofprobabilitycanbeusefultodeterminewhichteststoperform.ThemoststudiedclinicalpredictionruleistheWellsscore.DeepveinthrombosisDiagnosisDeepveinthrombosisDiagnosisPhysicalExam:symptomsHalfoft...