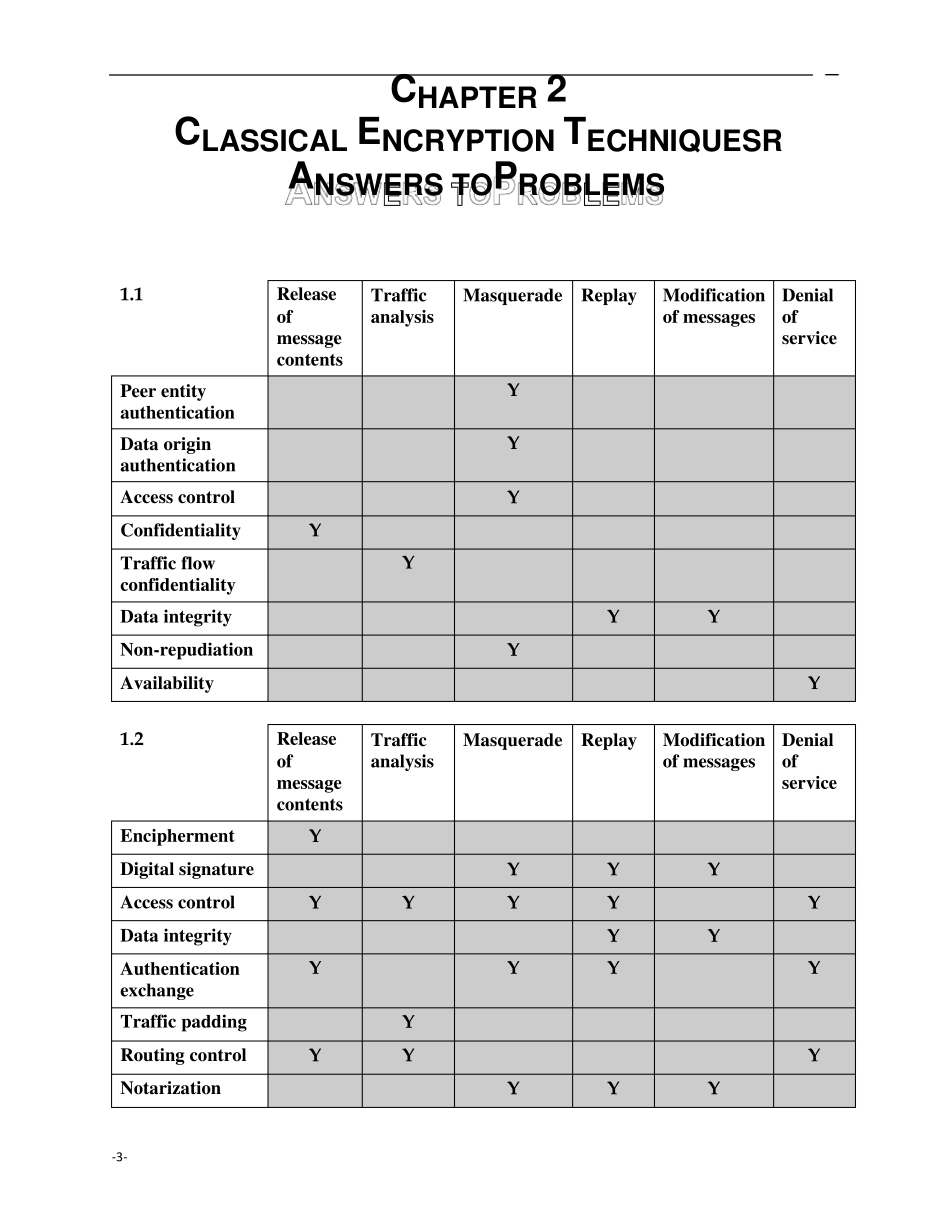
ANSW ERS TO QUESTIONS 1.1 The OSI Security Architecture is a framework that provides a systematic way of defining the requirements for security and characterizing the approaches to satisfying those requirements. The document defines security attacks, mechanisms, and services, and the relationships among these categories. 1.2 Passiv e attacks have to do with eavesdropping on, or monitoring, transmissions. Electronic mail, file transfers, and client/server exchanges are examples of transmissions that can be monitored. Activ e attacks include the modification of transmitted data and attempts to gain unauthorized access to computer systems. 1.3 Passiv e attacks: release of message contents and traffic analysis. Activ e attacks: masquerade, replay, modification of messages, and denial of service. 1.4 Authentication: The assurance that the communicating entity is the one that it claims to be. Access control: The prevention of unauthorized use of a resource (i.e., this service controls who can have access to a resource, under what conditions access can occur, and what those accessing the resource are allowed to do). Data confidentiality: The protection of data from unauthorized disclosure. Data integrity: The assurance that data received are exactly as sent by an authorized entity (i.e., contain no modification, insertion, deletion, or replay). Chapter 1: Introduction ..................................................................................................5 Chapter 2: Classical Encryption Techniques ...............................................................7 Chapter 3: Block Ciphers and the Date Encryption Standard ................................13 Chapter 4: Finite Fields ...................................................................