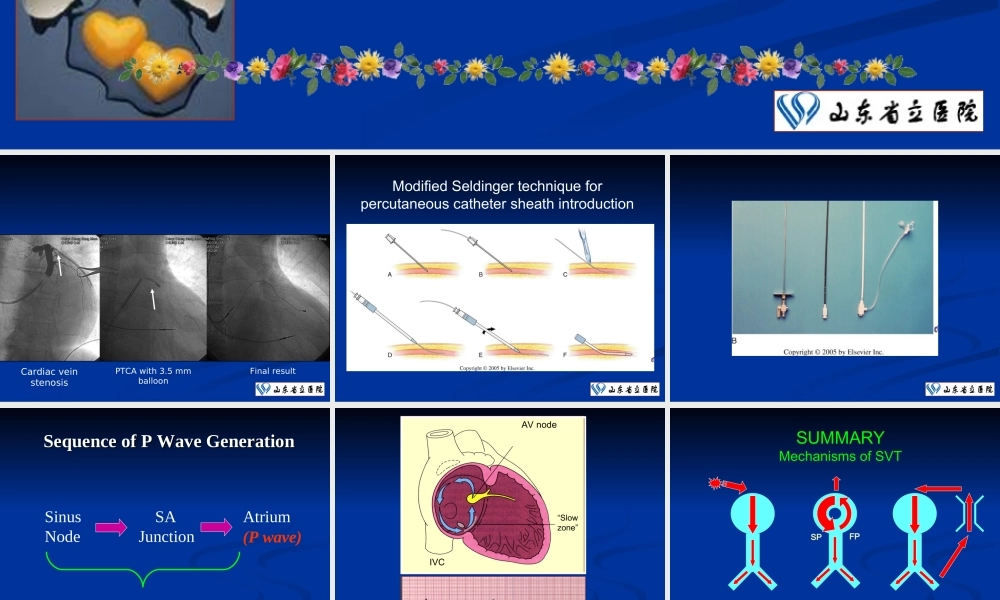
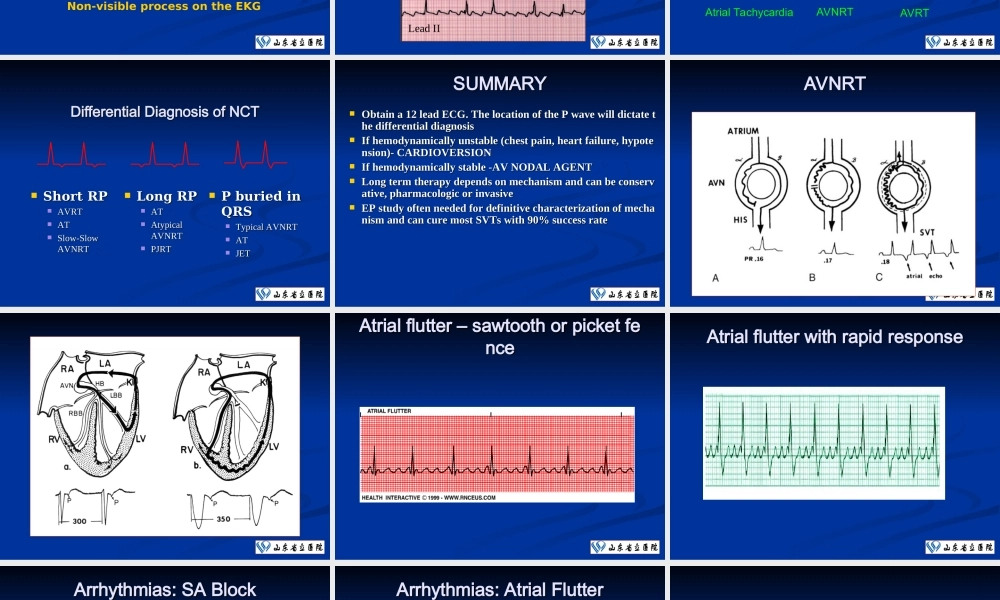
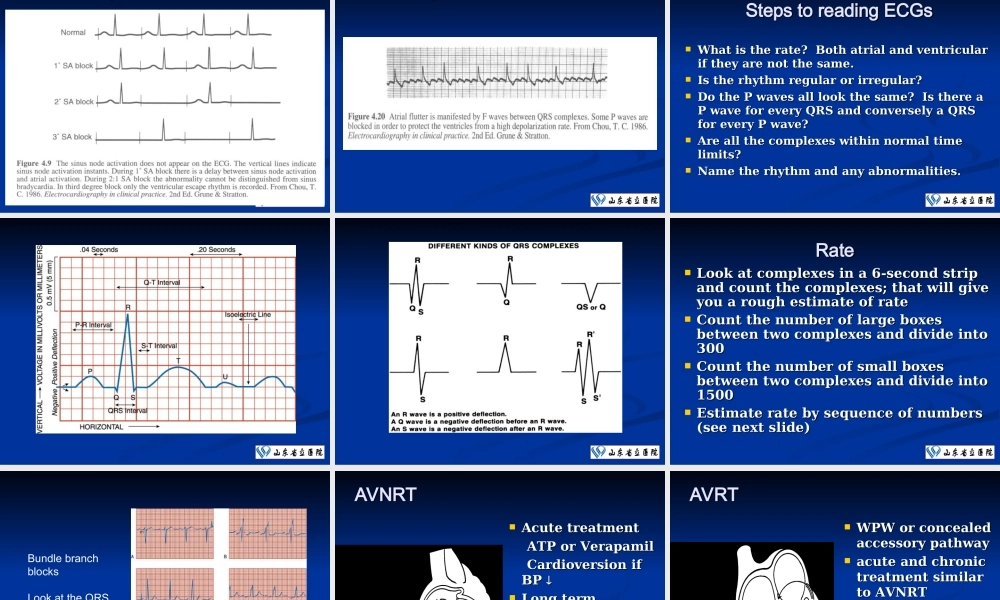
电生理相关资料电生理相关资料 Cardiac vein stenosisPTCA with 3.5 mm balloonFinal result Modified Seldinger technique for percutaneous catheter sheath introduction Sequence of P Wave GenerationSequence of P Wave GenerationSinus Node SAJunctionAtrium(P wave)Non-visible process on the EKG AV node“Slowzone”IVCLead II SUMMARYMechanisms of SVTAtrial TachycardiaAVNRTAVRTFPSP Differential Diagnosis of NCTDifferential Diagnosis of NCT Short RPShort RP AVRTAVRT ATAT Slow-Slow Slow-Slow AVNRTAVNRT Long RPLong RP ATAT Atypical Atypical AVNRTAVNRT PJRTPJRT P buried in P buried in QRSQRS Typical AVNRTTypical AVNRT ATAT JETJET SUMMARYSUMMARY Obtain a 12 lead ECG. The location of the P wave will dictate tObtain a 12 lead ECG. The location of the P wave will dictate the differential diagnosishe differential diagnosis If hemodynamically unstable (chest pain, heart failure, hypoteIf hemodynamically unstable (chest pain, heart failure, hypotension)- CARDIOVERSIONnsion)- CARDIOVERSION If hemodynamically stable -AV NODAL AGENTIf hemodynamically stable -AV NODAL AGENT Long term therapy depends on mechanism and can be conservLong term therapy depends on mechanism and can be conservative, pharmacologic or invasive ative, pharmacologic or invasive EP study often needed for definitive characterization of mechaEP study often needed for definitive characterization of mechanism and can cure most SVTs with 90% success ratenism and can cure most SVTs with 90% success rate AVNRTAVNRT Atrial flutter – sawtooth or picket feAtrial flutter – sawtooth or picket fencence Atrial flutter with rapid responseAtrial flutter with rapid response Arrhythmias: SA BlockArrhythmias: SA BlockPQRS T Arrhythmias: Atrial FlutterArrhythmias: Atrial Flutt...