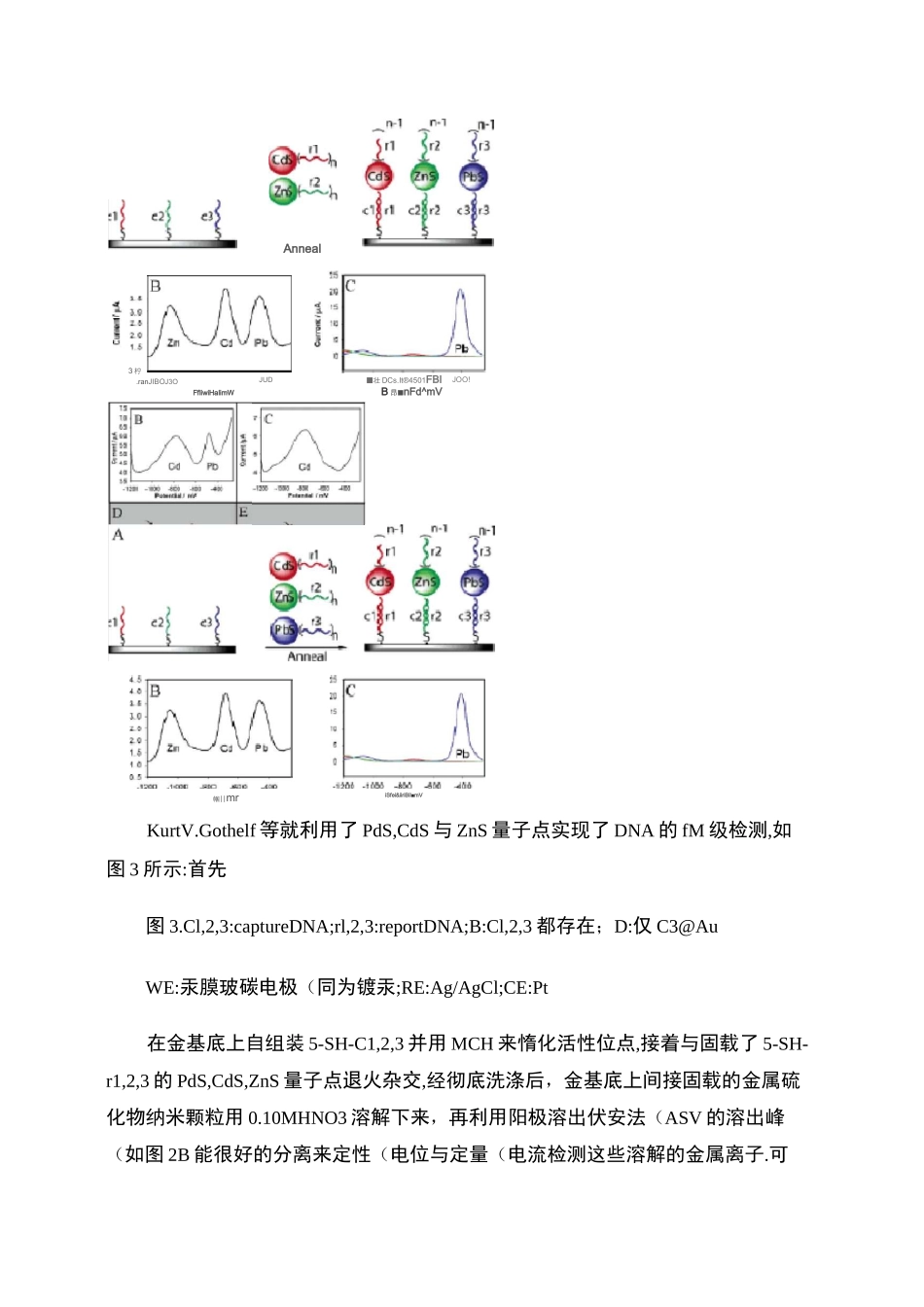
DNA 电化学传感器DNA 的分析对临床医学和遗传工程的研究具有深远的意义和应用价值,已逐渐成为分子生物学,生物技术和临床医学研究的重要领域•其中电化学 DNA 传感器依靠生物体内物质间特有的亲合力快速、直接获取复杂体系组成信息,具有选择性好、种类多、测试费用低及适合联机化的优点,又有电分析化学的不破坏测试体系、不受颜色影响和简便的特点,能广泛应用于医疗、工业生产、环境监测等领域,已倍受青睐.电化学 DNA 传感器的种类很多,具体和类型的优缺点如下表所示:Table1ComparisonofplatformsforDNAelectrochemicalsendingTypeofsensorAdvantagesDisadvantagesDirectDNAelectrochemistryHighlysensitive(femtomolesoftarget];requiresnolabeling-step;amenabletoarangeofelectrodesHighbackgrourdestroysthe 阴 iIndirectDNAelectrochemistryHighlysensitive(attomolesoftarget);usuallyrequiresnolabelingstep;multiple-targetdetectionatsameelectrodeProbesubstratethesampleDNA-specificredoxindicatordetectionModeratetohighsensitivityCfemtornolesoftarget];wellsuitedtomultiple-targetdetection;samplesremainunalteredChemicallabelimethodused;sNanoparticle-basedelectrochemistryamplificationExtremelysensitive(femtomoletozeptorrioleran^ef10-IFto10_2imales);wellsuitedtomultiple-targetdetectionwithdifferentnanoparticlesManydevelopsrobustnessofsiusuallydestroysDNA-mediatedchargetransportHighlysensitive(femtomolerange)andsimpleassaysrequiresnolabelinguniquelywellsuitedformismatchdetection:sequenceindependent;amenabletomultiplexingjapplicabletoDNA-proteinsensingstepBiochemicalpr最早的电化学 DNA 传感器是利用 DNA 的直接电化学检测的,但由于碱基(G,C 氧化过电位比较大,很难实用•后来多利用间接的方法来实现 DNA 的电化学检测,基本原理如图 1 所示,即根据杂交前后杂交指示剂嵌入的量不同,进而产生与分析物浓度相关的电化学信号,实现目标物的检测•TypeofsensorAdvantagesDirisctDNAelectrcchemistiyHighlys^nsitrvQ(fentomolesoftarget);requiresnolabelingstep^amenabletoarangeofelectrodesIndirectDNAelectrochemistryHighlyiensitrve(attomolescftarget^usuallyrequiresnolabelingst«p:multiple-tar^tdetectionatsameclo