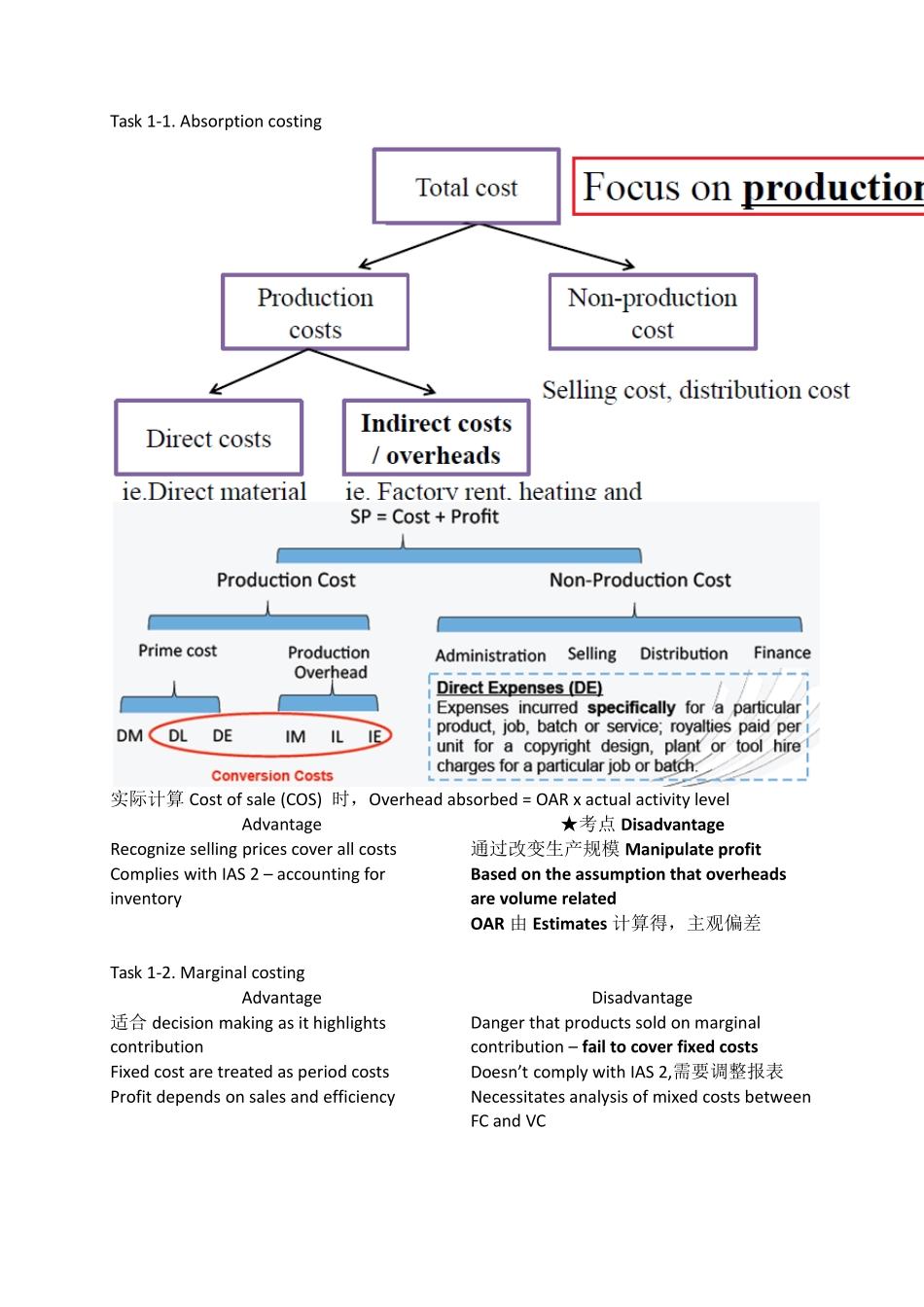
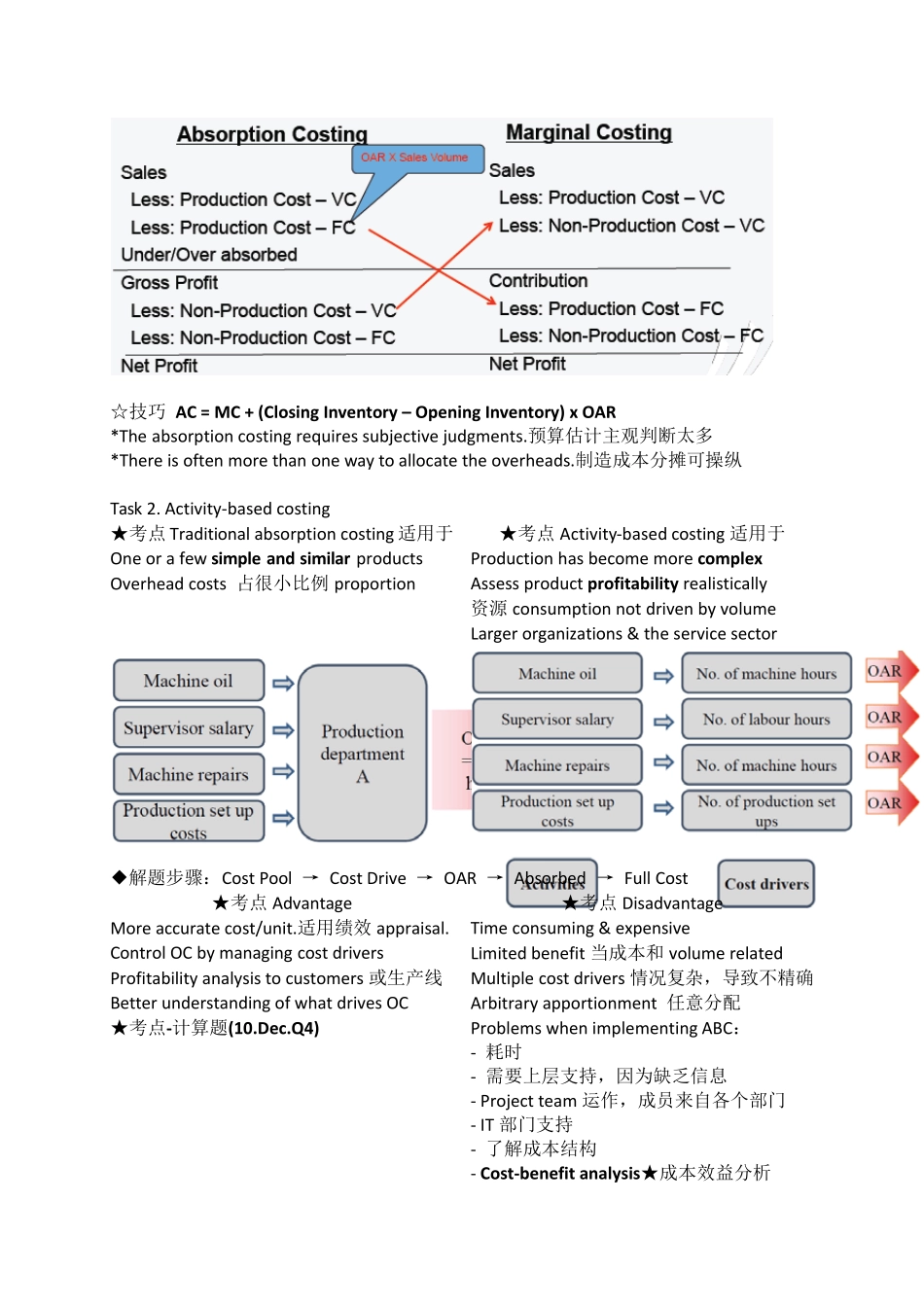
Task 1‐1. Absorption costing OAR= Estimated Production Overhead / Estimated Activity Level,都是budget 值 *Activity level 可以是production units,可以是labor hours,也可是machine hours 取决于劳动密集,还是机械生产密集intensive. 实际计算Cost of sale (COS) 时,Overhead absorbed = OAR x actual activity level Advantage ★考点 Disadvantage Recognize selling prices cover all costs 通过改变生产规模 Manipulate profit Complies with IAS 2 – accounting for inventory Based on the assumption that overheads are volume related OAR 由 Estimates 计算得,主观偏差 Task 1‐2. Marginal costing Advantage Disadvantage 适合 decision making as it highlights contribution Danger that products sold on marginal contribution – fail to cover fixed costs Fixed cost are treated as period costs Doesn’t comply with IAS 2,需要调整报表 Profit depends on sales and efficiency Necessitates analysis of mixed costs between FC and VC ☆技巧 AC = MC + (Closing Inventory – Opening Inventory) x OAR *The absorption costing requires subjective judgments.预算估计主观判断太多 *There is often more than one way to allocate the overheads.制造成本分摊可操纵 Task 2. Activity‐based costing ★考点Traditional absorption costing 适用于★考点Activity‐based costing 适用于 One or a few simple and similar products Production has become more complex Overhead costs 占很小比例proportion Assess product profitability realistically 资源consumption not driven by volume Larger organizations & the service sector 成本驱动drive:不同单位,不同OAR ◆解题步骤:Cost Pool → Cost Drive → OAR → Absorbed → Full Cost ★考点Advantage ★考点Disadvantage More accurate cost/unit.适用绩效 appraisal.Time consuming & expensive Control OC by managing cost drivers Limited benefit 当成本和 volume related Profitability analysi...