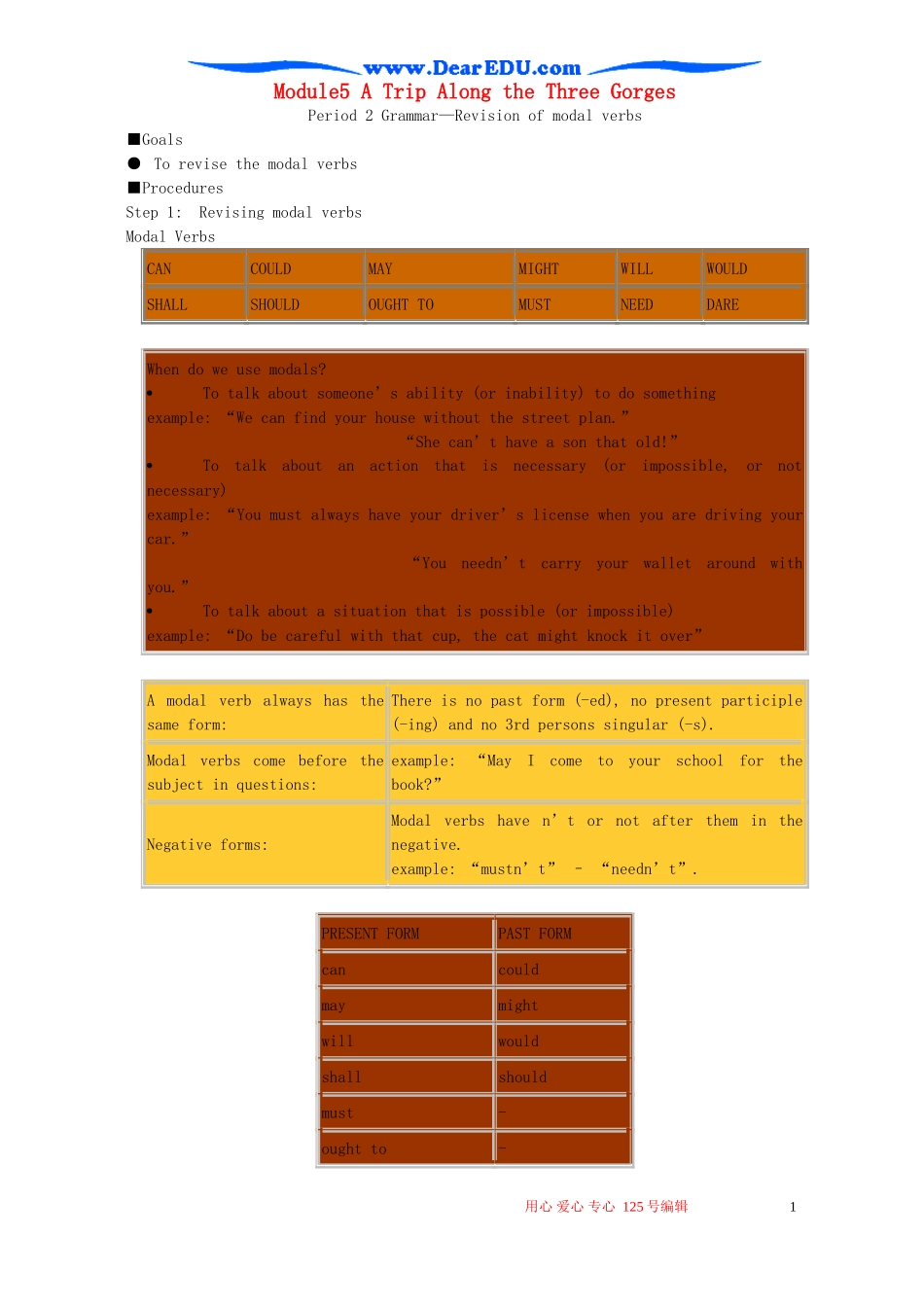
Module5 A Trip Along the Three GorgesPeriod 2 Grammar—Revision of modal verbs■Goals ● To revise the modal verbs■ProceduresStep 1: Revising modal verbsModal VerbsCANCOULDMAYMIGHTWILLWOULDSHALLSHOULDOUGHT TOMUSTNEEDDARE When do we use modals? To talk about someone’s ability (or inability) to do something example: “We can find your house without the street plan.” “She can’t have a son that old!” To talk about an action that is necessary (or impossible, or not necessary) example: “You must always have your driver’s license when you are driving your car.” “You needn’t carry your wallet around with you.”To talk about a situation that is possible (or impossible) example: “Do be careful with that cup, the cat might knock it over” A modal verb always has the same form:There is no past form (-ed), no present participle (-ing) and no 3rd persons singular (-s).Modal verbs come before the subject in questions:example: “May I come to your school for the book?”Negative forms:Modal verbs have n’t or not after them in the negative. example: “mustn’t” – “needn’t”. PRESENT FORMPAST FORMcancouldmaymightwillwouldshallshouldmust-ought to-用心 爱心 专心 125 号编辑 1 need-Step 2: Revising other uses of modal verbsApart from being used to describe degrees of certainty, modal verbs can also be used in the following ways: Obligation, prohibition and lack of obligation We use must to convey strong obligation. The past form of must for obligation is had to: You must improve your English handwriting! We had to leave his farm immediately.We use should to convey milder obligation. The past form of should for mild obligation is should have: You should see a lawyer. You should have gone to visit your ...