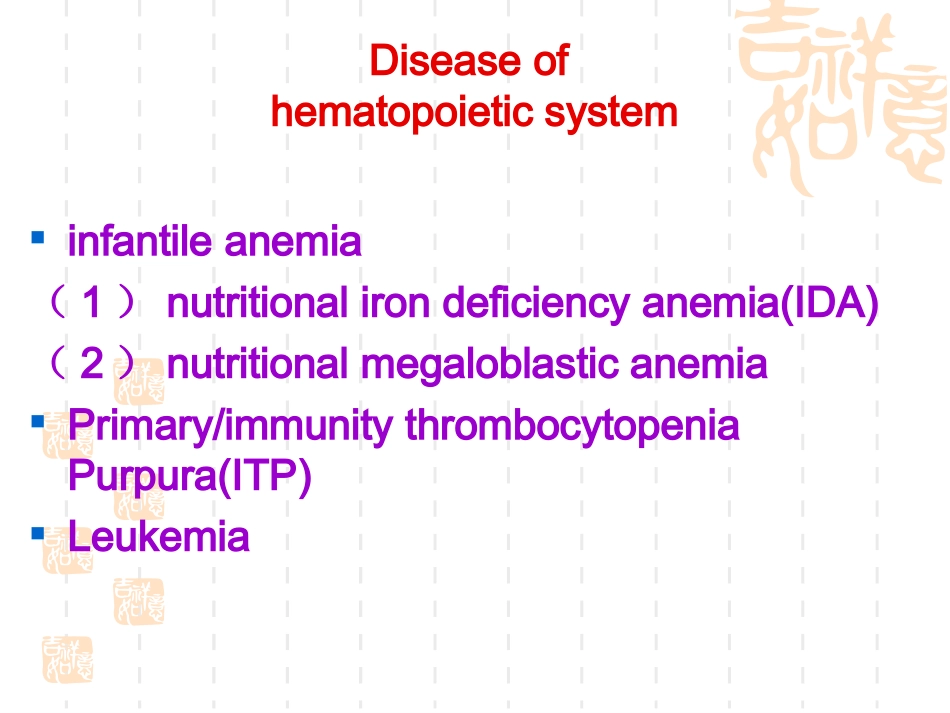
Anemiainchildhood(小儿贫血)Tounderstandfeaturesofhematopoiesisandbloodinchildren.Tocomprehendclinicalfeatures,diagnosisandtherapyofanemia.Tounderstandthedefinition,gradedivisionandclassificationofanemiainchildren.Tomasteretiology,pathogeny,diagnosis,therapyandpreventionofnutritionalirondeficiencyanemiaandnutritionalmegaloblasticanemia.Diseaseofhematopoieticsysteminfantileanemia(1)nutritionalirondeficiencyanemia(IDA)(2)nutritionalmegaloblasticanemiaPrimary/immunitythrombocytopeniaPurpura(ITP)Leukemiahaematogenesisofchildrenhematopoiesis--producedbloodextramedullarybeforebirthandpostnatalmesoblasthepaticmedullary3-15w6w-6ms3msEmbryostageMesoblastichaematogenesis:3wsbegin,8wsweaken,12-15wsdisappears。liver:8wsbegin,6monthsgraduallyweaken,erythroblast、granularcellandmegakaryocyte.Embryostage3、spleen:12wsbeginerythrocyte,granule,lymphocyte4、Haematogenesisoflymphaticorgan1.thoracicgland:8ws2.lymphaticnodes:11wsEmbryostage5、myelo-haematopoiesis:6monsHaematogenesisfunctionemphasis,makevariouskindsofbloodcells,uniquehematogenicorganafterbirth.Haematopoiesispostnatal1、marrow:2、extramedullary:whenrequirementofhaemopoiesisincrease,liver、spleen、lymphadenectasis,hepatomegalyandsplenomegaly,incirculatingbloodimmatureerythrocytesandgranulocytes.PhysiologicalhaemolysisNormalnewbornshavehigherhemoglobin(HB)andhematocritlevelsandashortenedsurvivalperiodofthefetalRBCscontributestothedevelopmentofphysiologicanemia.Physiologicalhaemolysiserythropoiesisabruptlyceaseswithonsetofrespirationatbirth,whenthearterialoxygensaturationrisestoward95%.levelsoferythropoietin(EPO)arelow.EPOhasadecreasedhalf-lifeandanincreasedvolumeofdistributioninnewborns.AshortenedsurvivalofthefetalRBCalsocontributestothedevelopmentofphysiologicanemia.thesizableexpansionofbloodvolumethataccompaniesrapidweightgainduringthefirst3mooflifeaddstotheneedforincreasedRBCproduction.bloodcharacteristics–agesredbloodcells(RBC)andHbPhysiologicalhaemolysisandanemiawritebloodcells(WBC)andclassification4-6crossPlatelets150-250×109/Lbloodvolume8-10%Redbloodcell(RBC)Termnewbornshavearedcellmassthatishigherthanatanyothertimeoflife.anappropriateconditionforthelowoxygenenvironmentofintrauterinelife.TheRBCcountis5.0×1012~7.0×1012,hemoglobinconcentrationisabout150~220g/Latbirth.TheRBCandhemoglobinconcentrationinpreterminfantsareslightlylowerthanthoseinterminfants.Redbloodcell(RBC)Thewiderangeofhemoglobinconcentrationisaccountedforby:Variationinhowrapidlytheumbilicalcordisclamped.Aninfant’spositionafterdelivery.Ifcordclampingisdelayedandthebabyisheldlowerthanplacenta,bothhemoglobinandbloodvolumeareincreasedbyaplacentaltransfusion.ChangeofHBafterbirthHgB2001801601401201008060401d5d10d2m3m7y12yReticulocyteReticulocyteReticulocyteis0.04-0.06inthefirst3days.Reticulocytedecreasesto0.005-0.015after4-7days.Reticulocyterisesto0.02-0.08in4-6weeks.Reticulocyteisequaltoanadult’safter5months.Whitebloodcell(WBC)ThenormalnumberofWBCishigherininfancyandearlychildhoodthanlaterinlife.WBCcountis15×109~20×109atbirth.After6~12hours,itriseto21×109~28×109andthenbeginstodecreaseto12×109by1week.WBCcountmaintainsabout10×109atinfantperiodandapproachadult’sWBCcountlevelby8years.Whitebloodcell(WBC)ThechangeinWBCclassificationistheproportionbetweenlymphocyteandgranu...