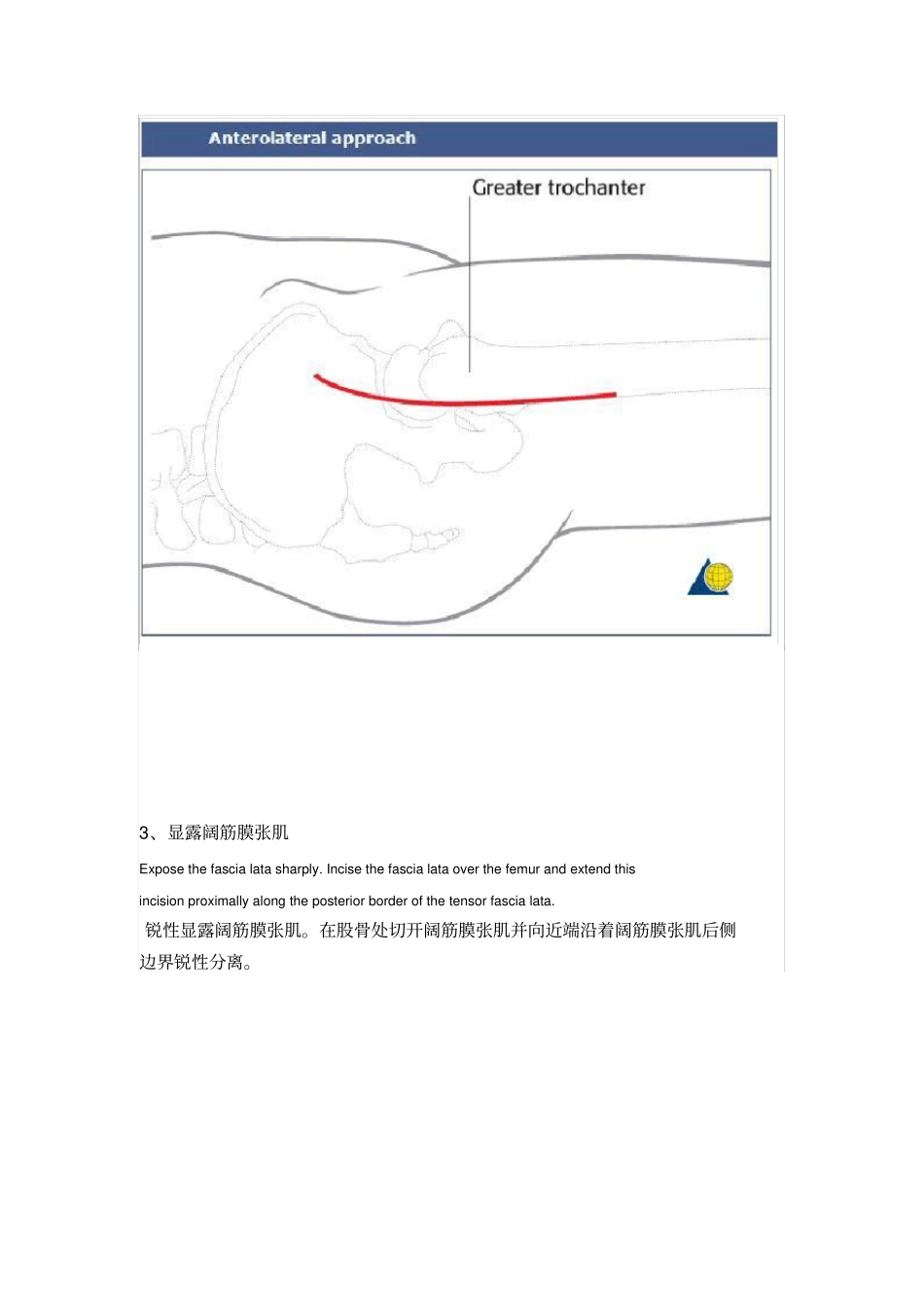
1、术前准备The anterolateral approach (Watson-Jones) to the proximal femur, through the interval between glutei and tensor fascia lata provides somewhat limited access to the hip joint along with the lateral proximal femur. With well-positioned retractors and adequate soft-tissue releases, it is possible to perform open reduction of displaced femoral neck fractures (31-B), and some femoral head fractures (31-C). A more medial approach to the hip joint (Iliofemoral or Smith-Peterson), medial to the tensor fascia lata, may improve access to the femoral head and neck, but for fixation of the neck with a sliding hip screw, a separate lateral incision will be required. 前外侧入路即 W-J 入路显露股骨近端,通过臀肌与阔筋膜张肌之间有限显露髋关节及股骨近端。 在牵开器帮助和充分的软组织松解的情况下,可以用来复位股骨颈骨折( 31-b ),有时也可以复位些股骨头骨折(31-C )。一个更靠内侧显露髋关节的切口如Iliofemoral 切口或 S-P 切口,在阔筋膜张肌内侧,可以提供显露股骨头和股骨颈,但是如果用DHS 固定股骨颈骨折, 则需要一个独立的外侧切口。2 、皮肤切口Start the slightly anteriorly curved skin incision about 7-10 cm proximal of the lateral part of the greater trochanter (directed towards the tubercule of the iliac crest – the posterior landmark of tensor fascia lata origin). Distally, the incision extends along the femur about 10 cm below the greater trochanter. 在股骨大转子上约7-10cm 外侧略前方处行轻微弯曲皮肤切口(方向从髂结节到阔筋膜张肌起始部),向远端延伸至股骨干(大粗隆下10cm 处)。3、显露阔筋膜张肌Expose the fascia lata sharply. Incise the fascia lata over the femur and extend this incision proximally along the posterior border of the tensor fascia lata.锐性显露阔筋膜张肌。在股骨处切开阔筋膜张肌并向近端沿着阔筋膜张肌后侧边界锐性分离。4、深层分离With the greater trochanter and the gluteus...