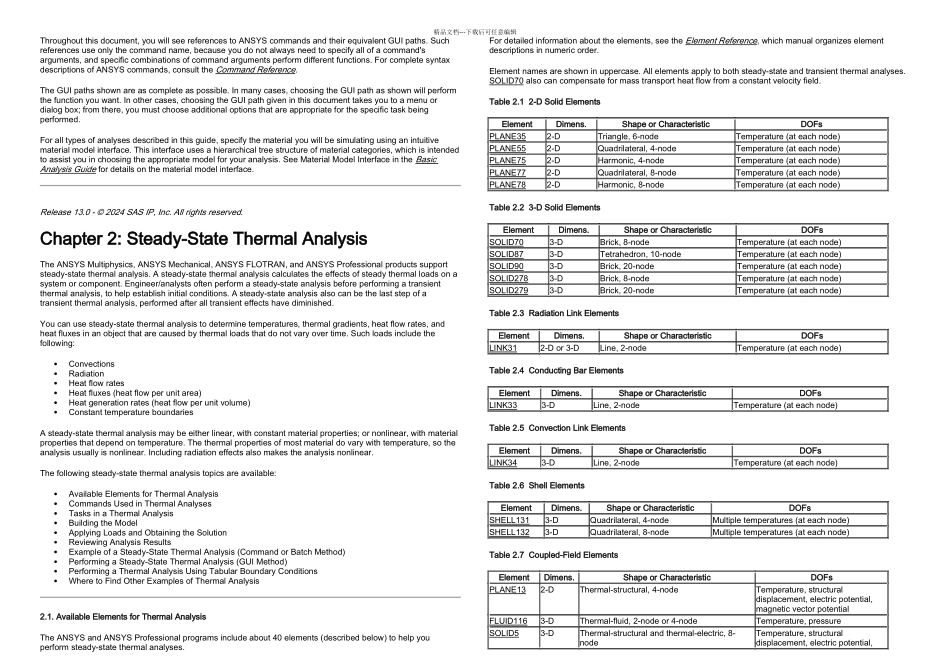
精品文档---下载后可任意编辑Release 13.0 - © 2024 SAS IP, Inc. All rights reserved.Table of Contents1. Analyzing Thermal Phenomena1.1. How ANSYS Treats Thermal Modeling. Convection. Radiation. Special Effects. Far-Field Elements1.2. Types of Thermal Analysis1.3. Coupled-Field Analyses1.4. About GUI Paths and Command Syntax2. Steady-State Thermal Analysis2.1. Available Elements for Thermal Analysis2.2. Commands Used in Thermal Analyses2.3. Tasks in a Thermal Analysis2.4. Building the Model. Using the Surface Effect Elements. Creating Model Geometry2.5. Applying Loads and Obtaining the Solution. Defining the Analysis Type. Applying Loads. Using Table and Function Boundary Conditions. Specifying Load Step Options. General Options. Nonlinear Options. Output Controls. Defining Analysis Options. Saving the Model. Solving the Model2.6. Reviewing Analysis Results. Primary data. Derived data. Reading In Results. Reviewing Results2.7. Example of a Steady-State Thermal Analysis (Command or Batch Method). The Example Described. The Analysis Approach. Commands for Building and Solving the Model2.8. Performing a Steady-State Thermal Analysis (GUI Method)2.9. Performing a Thermal Analysis Using Tabular Boundary Conditions. Running the Sample Problem via Commands. Running the Sample Problem Interactively2.10. Where to Find Other Examples of Thermal Analysis3. Transient Thermal Analysis3.1. Elements and Commands Used in Transient Thermal Analysis3.2. Tasks in a Transient Thermal Analysis3.3. Building the Model3.4. Applying Loads and Obtaining a Solution. Defining the Analysis Type. Establishing Initial Conditions for Your Analysis. Specifying Load Step Options. Nonlinear Options. Output Controls3.5. Saving the Model. Solving the Model3.6. Reviewing Analysis ...