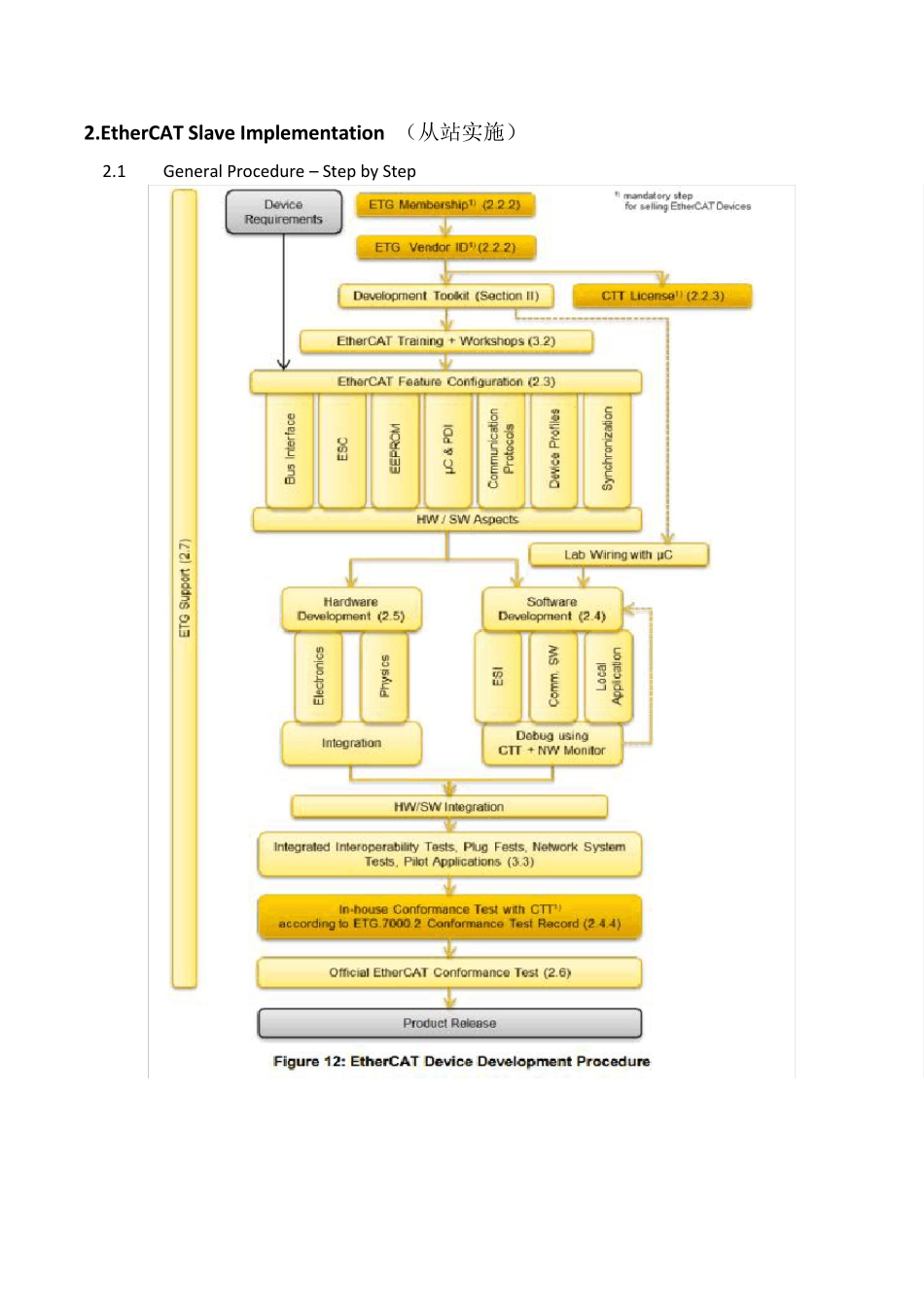
2.EtherCAT Slave Implementation (从站实施) 2.1 General Procedure – Step by Step 2.2 Administrative Organization(管理机构) 2.2.1 Development Time To develop a new running slave system, operated by a standard EtherCAT master, about 6-8 weeks are feasible. Herein, parts of the own application development are already included. The hardware design of the device depends on device type (with or without µ C) and the amount and type of ports (MII or LVDS). Table 4 shows the components needed for a slave device. 2.2.2 ETG Membership and Vendor ID(会员和厂商ID) 2.2.3 EtherCAT Conformance Test Tool License(一致性测试工具执照) 2.3 EtherCAT Slave Design (从站设计) EtherCAT features are to be selected according to the device requirements(需求). Thus, to develop an EtherCAT slave device, the developer should be conscious about the requirements of the device to decide which characteristic is to be chosen for every EtherCAT feature. In the following, an overview to the design criteria(设计准则) is given of which the ESC is the most important EtherCAT characteristic. The configuration of these criteria is finally stored(这个配置标准最后储存在) in the ESI file and the EEPROM. 2.3.1 Bus Interface to EtherCAT Netw ork(总线接口) 这需要决定于 ESC 的选择(相适应),一般一个独立的设备通过 100Base TX 或者100BaseFx 电缆连接到 Network 若要从从模块设备连到外部接口,一个 Converter(从 100Base 到 LVDS)是必需的 Application Note : A stand-alone device should support at least two MII ports (RJ45 or M12 D-Code connectors) to provide line connection. The logical port for connection is determined based on the number of ports being used. For standard 2 port usage, port0 and port1 are used. The PHYs should be selected according to(参考) th...